Elon Musk’s twitter account is seen through the Twitter logo in this illustration taken, April 25, 2022. REUTERS/Dado Ruvic/Illustration Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comNEW YORK, April 25 (Reuters) – Twitter Inc (TWTR.N) is poised to agree a sale to Elon Musk for around $43 billion in cash, the price the CEO of Tesla has called his “best and final” offer for the social media company, people familiar with the matter said.Twitter may announce the $54.20-per-share deal later on Monday once its board has met to recommend the transaction to Twitter shareholders, the sources said, adding it was still possible the deal could collapse at the last minute.Musk, the world’s richest person according to Forbes, is negotiating to buy Twitter in a personal capacity and Tesla (TSLA.O) is not involved in the deal.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comTwitter has not been able to secure so far a ‘go-shop’ provision under its agreement with Musk that would allow it to solicit other bids once the deal is signed, the sources said. Still, Twitter would be allowed to accept an offer from another party by paying Musk a break-up fee, the sources added.The sources requested anonymity because the matter is confidential. Twitter and Musk did not immediately respond to requests for comment.Twitter shares were up 4.5% in pre-market trading in New York at $51.15.Musk, a prolific Twitter user, has said it needs to be taken private to grow and become a genuine platform for free speech.The 50-year-old entrepreneur, who is also CEO of rocket developer SpaceX, has said he wants to combat trolls on Twitter and proposed changes to the Twitter Blue premium subscription service, including slashing its price and banning advertising.The billionaire, a vocal advocate of cryptocurrencies, has also suggested adding dogecoin as a payment option on Twitter.He has said Twitter’s current leadership team is incapable of getting the company’s stock to his offer price on its own, but stopped short of saying it needs to be replaced.”The company will neither thrive nor serve this societal imperative in its current form,” Musk said in his offer letter last week.Up to the point Musk disclosed a stake in Twitter in April, the company’s shares had fallen about 10% since Parag Agrawal took over as CEO from founder Jack Dorsey in late November.The deal, if it happens, would come just four days after Musk unveiled a financing package to back the acquisition.This led Twitter’s board to take his offer more seriously and many shareholders to ask the company not to let the opportunity for a deal slip away, Reuters reported on Sunday. Before Musk revealed the financing package, Twitter’s board was expected to reject the bid, sources had said. read more The sale would represent an admission by Twitter that Agrawal is not making enough traction in making the company more profitable, despite being on track to meet ambitious financial goals the company set for 2023. Twitter’s shares were trading higher than Musk’s offer price as recently as November.Musk unveiled his intention to buy Twitter on April 14 and take it private via a financing package comprised of equity and debt. Wall Street’s biggest lenders, except those advising Twitter, have all committed to provide debt financing.Musk’s negotiating tactics – making one offer and sticking with it – resembles how another billionaire, Warren Buffett, negotiates acquisitions. Musk did not provide any financing details when he first disclosed his offer for Twitter, making the market skeptical about its prospects.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Greg Roumeliotis in New York, additional reporting by Krystal Hu;
Editing by Mark PotterOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .
Analysis: Positive real yields may spell more trouble for U.S. stocks
A street sign for Wall Street is seen in the financial district in New York, U.S., November 8, 2021. REUTERS/Brendan McDermid/File Photo/File PhotoRegister now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comNEW YORK, April 20 (Reuters) – A hawkish turn by the Federal Reserve is eroding a key support for U.S. stocks, as real yields climb into positive territory for the first time in two years.Yields on the 10-year Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) – also known as real yields because they subtract projected inflation from the nominal yield on Treasury securities – had been in negative territory since March 2020, when the Federal Reserve slashed interest rates to near zero. That changed on Tuesday, when real yields ticked above zero. Negative real yields have meant that an investor would have lost money on an annualized basis when buying a 10-year Treasury note, adjusted for inflation. That dynamic has helped divert money from U.S. government bonds and into a broad spectrum of comparatively riskier assets, including stocks, helping the S&P 500 (.SPX) more than double from its post-pandemic low.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comAnticipation of tighter monetary policy, however, is pushing yields higher and may dent the luster of stocks in comparison to Treasuries, which are viewed as much less risky since they are backed by the U.S. government.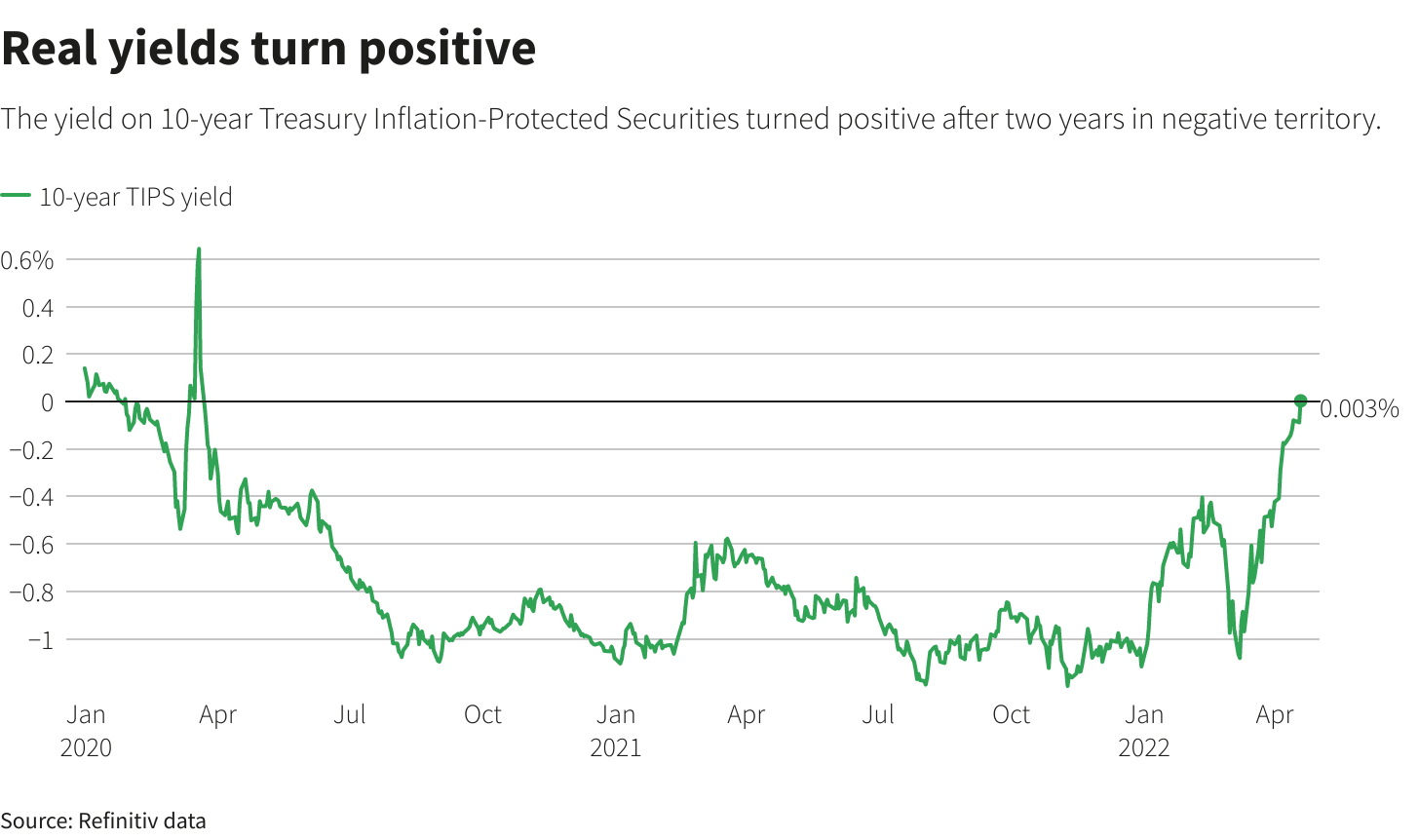 Reuters GraphicsOn Tuesday, stocks shrugged off the rise in yields, with the S&P 500 ending up 1.6% on the day. Still, the S&P 500 is down 6.4% this year, while the yield on the 10-year TIPS has climbed more than 100 basis points.”Real 10-year yields are the risk-free alternative to owning stocks,” said Barry Bannister, chief equity strategist at Stifel. “As real yield rises, at the margin it makes stocks less attractive.”One key factor influenced by yields is the equity risk premium, which measures how much investors expect to be compensated for owning stocks over government bonds.Rising yields have helped result in the measure standing at its lowest level since 2010, Truist Advisory Services said in a note last week.
Reuters GraphicsOn Tuesday, stocks shrugged off the rise in yields, with the S&P 500 ending up 1.6% on the day. Still, the S&P 500 is down 6.4% this year, while the yield on the 10-year TIPS has climbed more than 100 basis points.”Real 10-year yields are the risk-free alternative to owning stocks,” said Barry Bannister, chief equity strategist at Stifel. “As real yield rises, at the margin it makes stocks less attractive.”One key factor influenced by yields is the equity risk premium, which measures how much investors expect to be compensated for owning stocks over government bonds.Rising yields have helped result in the measure standing at its lowest level since 2010, Truist Advisory Services said in a note last week.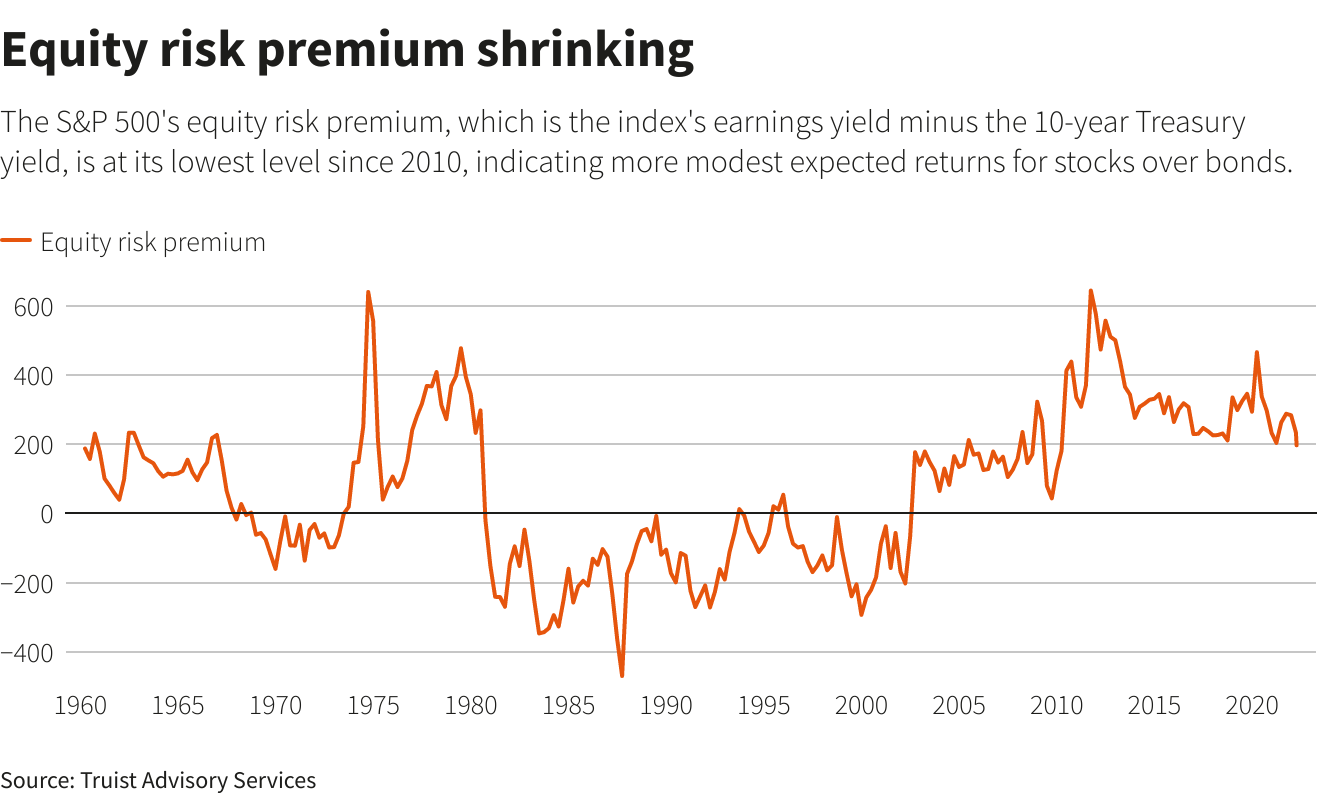 Reuters GraphicsHEADWIND TO GROWTH SHARESHigher yields in particular dull the allure of companies in technology and other high-growth sectors, with those companies’ cash flows often more weighted in the future and diminished when discounted at higher rates.That may be bad news for the broader market. The heavy presence of tech and other growth stocks in the S&P 500 means the index’s overall expected dividends are weighted in the future at close to their highest level ever, according to BofA Global Research. Five massive, high-growth stocks, for example, now make up 22% of the weight of the S&P 500.At the same time, growth shares in recent years have been highly linked to the movement of real yields.Since 2018, a ratio comparing the performance of the Russell 1000 growth index (.RLG) to its counterpart for value stocks (.RLV) – whose cash flows are more near-term – has had a negative 96% correlation with 10-year real rates, meaning they tend to move in opposite directions from growth stocks, according to Ohsung Kwon, a U.S. equity strategist at BofA Global Research.Rising yields are “a bigger headwind to equities than (they have) been in history,” he said.
Reuters GraphicsHEADWIND TO GROWTH SHARESHigher yields in particular dull the allure of companies in technology and other high-growth sectors, with those companies’ cash flows often more weighted in the future and diminished when discounted at higher rates.That may be bad news for the broader market. The heavy presence of tech and other growth stocks in the S&P 500 means the index’s overall expected dividends are weighted in the future at close to their highest level ever, according to BofA Global Research. Five massive, high-growth stocks, for example, now make up 22% of the weight of the S&P 500.At the same time, growth shares in recent years have been highly linked to the movement of real yields.Since 2018, a ratio comparing the performance of the Russell 1000 growth index (.RLG) to its counterpart for value stocks (.RLV) – whose cash flows are more near-term – has had a negative 96% correlation with 10-year real rates, meaning they tend to move in opposite directions from growth stocks, according to Ohsung Kwon, a U.S. equity strategist at BofA Global Research.Rising yields are “a bigger headwind to equities than (they have) been in history,” he said.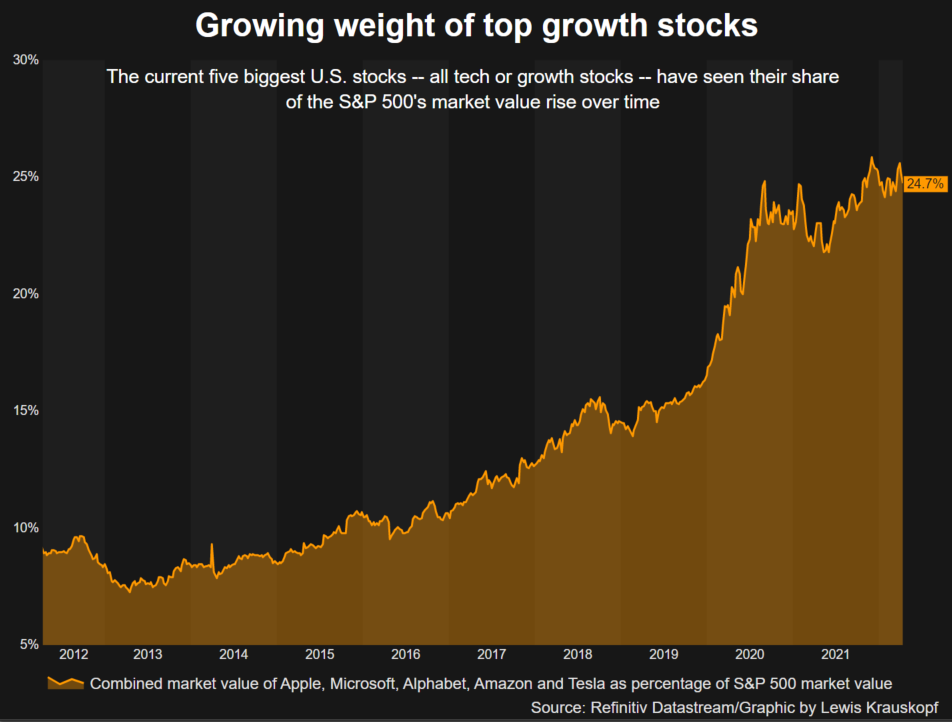 Top five stocks market cap as percentage of S&P 500Bannister estimates the S&P 500 could retest its lows of the year, which included a drop in March of 13% from the index’s record high, should the yield on the 10-year TIPS rise to 0.75% and the earnings outlook – a key component of the risk premium – remain unchanged.Lofty valuations also make stocks vulnerable if yields continue rising. Though the tumble in stocks has moderated valuations this year, the S&P 500 still trades at about 19 times forward earnings estimates, compared with a long-term average of 15.5, according to Refinitiv Datastream.“Valuations aren’t great on stocks right now. That means that capital may look at other alternatives to stocks as they become more competitive,” said Matthew Miskin, co-chief investment strategist at John Hancock Investment Management.Still, some investors believe stocks can survive just fine with rising real yields, for now. Real yields were mostly in positive territory over the past decade and ranged as high as 1.17% while the S&P 500 has climbed over 200%.JPMorgan strategists earlier this month estimated that equities could cope with 200 basis points of real yield increases. They advised clients maintain a large equity versus bond overweight.”If bond yield rises continue, they could eventually become a problem for equities,” the bank’s strategists said. “But we believe current real bond yields at around zero are not high enough to materially challenge equities.”Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Lewis Krauskopf in New York
Top five stocks market cap as percentage of S&P 500Bannister estimates the S&P 500 could retest its lows of the year, which included a drop in March of 13% from the index’s record high, should the yield on the 10-year TIPS rise to 0.75% and the earnings outlook – a key component of the risk premium – remain unchanged.Lofty valuations also make stocks vulnerable if yields continue rising. Though the tumble in stocks has moderated valuations this year, the S&P 500 still trades at about 19 times forward earnings estimates, compared with a long-term average of 15.5, according to Refinitiv Datastream.“Valuations aren’t great on stocks right now. That means that capital may look at other alternatives to stocks as they become more competitive,” said Matthew Miskin, co-chief investment strategist at John Hancock Investment Management.Still, some investors believe stocks can survive just fine with rising real yields, for now. Real yields were mostly in positive territory over the past decade and ranged as high as 1.17% while the S&P 500 has climbed over 200%.JPMorgan strategists earlier this month estimated that equities could cope with 200 basis points of real yield increases. They advised clients maintain a large equity versus bond overweight.”If bond yield rises continue, they could eventually become a problem for equities,” the bank’s strategists said. “But we believe current real bond yields at around zero are not high enough to materially challenge equities.”Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Lewis Krauskopf in New York
Editing by Ira Iosebashvili and Matthew LewisOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .
Ramsay Health Care gets $14.8 bln bid from KKR-led consortium; shares soar
Trading information for KKR & Co is displayed on a screen on the floor of the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) in New York, U.S., August 23, 2018. REUTERS/Brendan McDermidRegister now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.com
- Ramsay receives A$88 cash per share proposal
- Proposal at a 37% premium to Ramsay’s last close
- Ramsay stock up 29.8% in early trade
April 20 (Reuters) – Ramsay Health Care Ltd (RHC.AX), Australia’s largest private hospital operator, said on Wednesday it received a A$20.05 billion ($14.80 billion) indicative takeover offer from a consortium led by private equity giant KKR & Co (KKR.N).The non-binding proposal of A$88 cash per share represents a premium of nearly 37% to Ramsay’s Tuesday closing price of A$64.39. The offer sent the hospital operator’s shares up as much as 29.8% to A$83.55 in early trade, their biggest-ever intraday jump.Ramsay said in a statement it would provide the KKR-led consortium with due diligence on a non-exclusive basis and talks were at a preliminary stage.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comThe hospital operator said it had reviewed the proposal with its advisers and asked for further information from the consortium in relation to its funding and structure of the deal.KKR did not immediately respond to a Reuters request for comment.If successful, the takeover would be the biggest in Australia this year and nearly double deal activity, which at a total value of $17.4 billion, suffered a 41.2% decline in the first quarter compared with a year earlier, according to Refinitiv data.The proposal comes as record-low interest rates prompt private equity firms, superannuation and pension funds with ample liquidity to invest in healthcare and infrastructure assets.The deal would also rank as the second biggest private-equity backed in deal in Australia, following a consortium’s A$31.6 billion ($23.35 billion) enterprise value deal for Sydney airport last year. read more The pandemic hit healthcare operators including Ramsay, with the shutdown of non-urgent surgeries, staffing shortages due to isolation regulations, and upward wage pressure weighing on earnings and hurting stocks, making the sector relatively affordable for a buyout, compared to a few years ago.Last year, Australian biopharmaceutical giant CSL Ltd (CSL.AX) said it would buy Swiss drugmaker Vifor Pharma AG (VIFN.S) for $11.7 billion. read more Ramsay operates hospitals and clinics across 10 countries in three continents, with a network of more than 530 locations, according to its website.It has 72 private hospitals and day surgery units in Australia, while it operates clinics and primary care units in about 350 locations across six countries in Europe.KKR currently owns French healthcare group Elsan.Earlier this year, Ramsay and Malaysia’s Sime Darby Holdings received a $1.35 billion buyout offer from IHH Healthcare Bhd (IHHH.KL) for their Asia joint venture. Ramsay said it was still pursuing this transaction. The hospital operator has hired UBS AG’s Australia Branch and Herbert Smith Freehills as financial and legal advisers, respectively, for the KKR-led consortium’s proposal.($1 = 1.3535 Australian dollars)Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Harish Sridharan in Bengaluru; additional reporting by Byron Kaye in Sydney; Editing by Sriraj Kalluvila, Aditya Soni and Krishna Chandra Eluri and Rashmi AichOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .
Benetton team working on premium of around 30% to buy out Atlantia – sources
The logo of infrastructure group Atlantia in Rome, Italy October 5, 2020. REUTERS/Guglielmo MangiapaneRegister now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comMILAN, April 12 (Reuters) – The Benetton family and U.S. investment fund Blackstone are working on a premium of around 30% over Atlantia’s (ATL.MI) average stock price in the last six months, as they ready a bid that could land as early as Wednesday, three sources said.The two partners are considering an offer between 22 and 23 euros per share, one of the sources said, but cautioned no final decision had been taken.While a significant premium on the six month average share price, that would be a more modest increase over the current price of about 21.7 euros, and would value the whole of Atlantia – in which the Benetton family already owns a 33% stake – at about 18.1-19.0 billion euros ($19.7-$20.7 billion).Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comShares in the Italian infrastructure group have gained nearly 20% since April 6 when speculation first emerged about an approach involving Global Infrastructure Partners (GIP), Brookfield and Florentino Perez, head of Spain’s ACS (ACS.MC).The stock hit a two-year high of 22.5 euros on Monday as investors waited for a move that could take the group private.”The offer could land very soon, even early Wednesday morning,” one of the sources said.Blackstone and Benetton holding company Edizione declined to comment.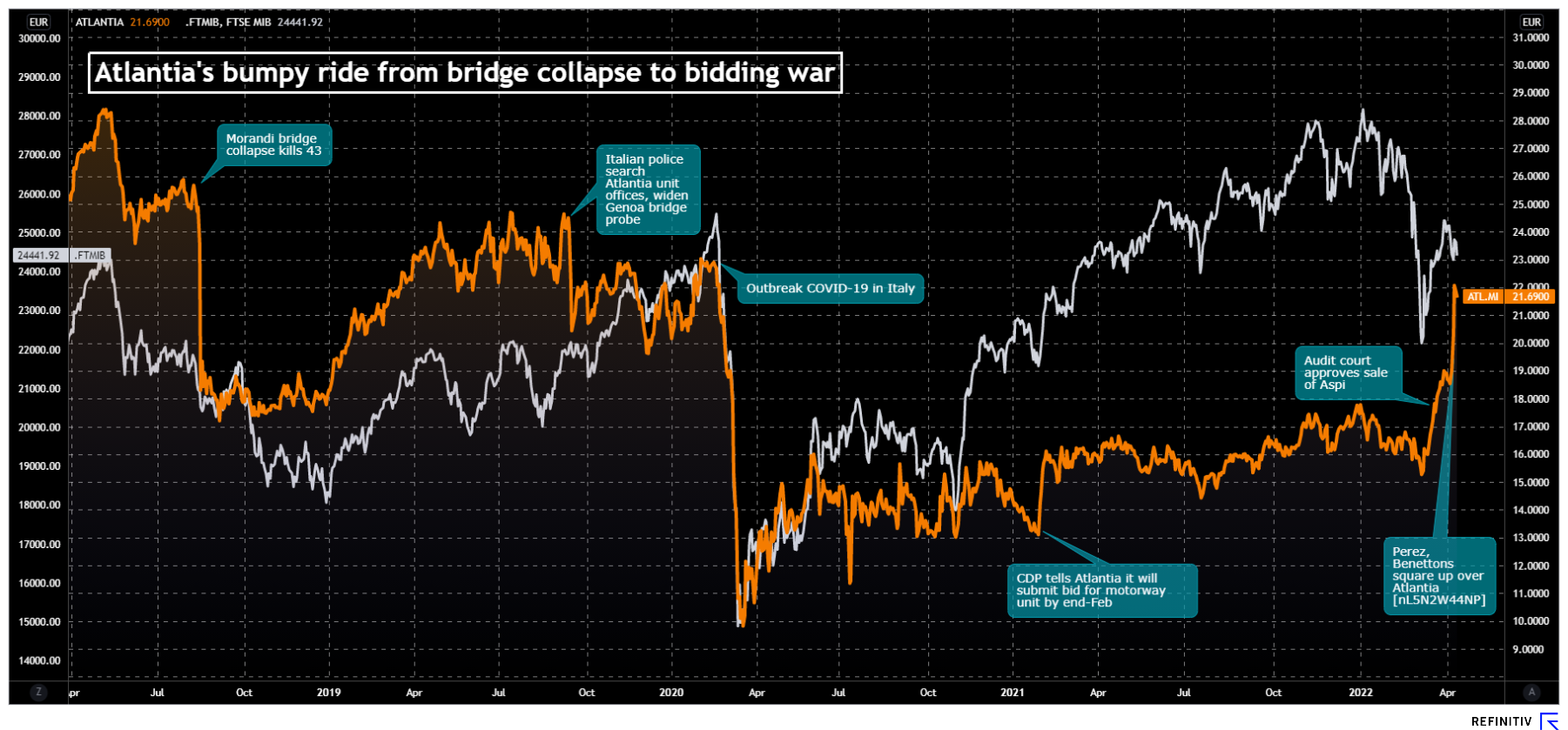 Atlantia’s share performanceEdizione and Blackstone want to delist Atlantia to shield it from the appetite of rival suitors, who approached the Benettons last month with a proposal to buy the group and hand over Atlantia’s motorway concessions to Perez.GIP, Brookfield and the Spanish tycoon are in a ‘wait and see’ mode after the Benetton family and Atlantia’s long-time investors CRT and GIC rebuffed their offer, sources have said.The takeover offer comes as Atlantia prepares to pocket 8 billion euros from the sale of the group’s Italian motorway unit, a deal aimed at ending a political dispute triggered by the 2018 collapse of a motorway bridge.It also puts the spotlight on Alessandro Benetton, 58, who was appointed chairman of Edizione earlier this year, tightening the family’s grip on its investments.After parting ways with its Autostrade per l’Italia, Atlantia will continue to run airports in Italy and France, motorways in Europe and Latin America and digital toll payment company Telepass.The Italian government so far has been silent on the latest developments, but it has special vetting ‘golden’ powers over strategic assets, such as the country’s airports and their ownership.($1 = 0.9184 euro)Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Francesca Landini and Stephen Jewkes
Atlantia’s share performanceEdizione and Blackstone want to delist Atlantia to shield it from the appetite of rival suitors, who approached the Benettons last month with a proposal to buy the group and hand over Atlantia’s motorway concessions to Perez.GIP, Brookfield and the Spanish tycoon are in a ‘wait and see’ mode after the Benetton family and Atlantia’s long-time investors CRT and GIC rebuffed their offer, sources have said.The takeover offer comes as Atlantia prepares to pocket 8 billion euros from the sale of the group’s Italian motorway unit, a deal aimed at ending a political dispute triggered by the 2018 collapse of a motorway bridge.It also puts the spotlight on Alessandro Benetton, 58, who was appointed chairman of Edizione earlier this year, tightening the family’s grip on its investments.After parting ways with its Autostrade per l’Italia, Atlantia will continue to run airports in Italy and France, motorways in Europe and Latin America and digital toll payment company Telepass.The Italian government so far has been silent on the latest developments, but it has special vetting ‘golden’ powers over strategic assets, such as the country’s airports and their ownership.($1 = 0.9184 euro)Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Francesca Landini and Stephen Jewkes
Editing by Mark Potter and Chizu NomiyamaOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .
Japan buyers agree to Q2 aluminium premium of $172/T, sources say
Containers are seen at an industrial port in the Keihin Industrial Zone in Kawasaki, Japan September 12, 2018. REUTERS/Kim Kyung-HoonRegister now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.com
- Initial offers made by producers were $195-$250/T
- Second straight quarterly price fall
- Contrast to soaring premiums in Europe and the U.S.
TOKYO, April 7 (Reuters) – The premium for aluminium shipments to Japanese buyers for April to June was set at $172 a tonne, down 2.8% from the previous quarter, as weak demand in Japan and China outweighed concerns of supply disruptions from Russia, five sources said.The figure is lower than the $177 per tonne paid in the January-March quarter and marks a second consecutive quarterly drop. It is also lower than initial offers of $195-$250 made by producers. read more Japan is Asia’s biggest aluminium importer and the premiums for primary metal shipments it agrees to pay each quarter over the benchmark London Metal Exchange (LME) cash price set the benchmark for the region.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comThe sources, who were directly involved in pricing talks, declined to be identified because of the sensitivity of the discussions.One of them, who works at a Japanese trading house, said the decline in premiums reflected weak demand from the automobile sector as it deals with a chip shortage, as well as amply supply in Asia as China has increased exports of semi-manufactured metals.A tight container market and high freight rates also made it difficult for the metal to be shipped from Asia to Europe or North America where premiums are much higher, the source said.China is increasing exports of aluminium to fill a widening supply gap in Western markets. read more Global suppliers such as Rio Tinto (RIO.AX) and South32 (S32.AX) and Japanese manufacturers of rolled products and trading houses began price negotiations in early March. The talks took longer than usual because of uncertainty about exports from Russia as a result of sanctions following its invasion of Ukraine.Russia accounted for 17% of Japan’s total imports of primary aluminium ingots in 2021 and 6% of global aluminium supply.Concerns about the impact of disrupted Russian shipments as well as reduced output because of high power prices drove aluminium prices to a record high of $4,073.50 a tonne in early March.The duty-paid physical premiums in Europe and the United States have soared to $595 a tonne and $880 a tonne, respectively, while Asia’s spot premiums have remained around $110-170 a tonne this year, the sources said.Another of the sources said so far Russia’s Rusal had maintained shipments to Japan, which made global suppliers retreat from high initial offers.However, another of the sources said Asian supplies might get tighter as “global traders have been collecting primary aluminium from several locations in Asia and sending them to Europe or North America by chartering bulk ships to take an advantage of higher premiums”.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Yuka Obayashi; Editing by Himani Sarkar and Barbara LewisOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .










