BRASILIA, July 22 (Reuters) – Brazilian fixed-income markets are pricing in the highest risk levels in years, raising red flags among investors and government officials who see little relief in sight.While global interest rate hikes and recession risks have put all emerging markets under pressure, Brazil faces special scrutiny after Congress cracked open a constitutional spending cap to allow a burst of election-year expenditures. read more “The problem is the change in the spending cap,” said an Economy Ministry official, who requested anonymity to discuss the situation openly. “It weakens the reading that the fiscal situation will be under control in the coming years.”Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comEven with positive surprises such as strong June tax revenue data on Thursday, the official said Brazil’s yield curve remains under pressure as investors brace for the worst. read more Both major presidential candidates on the ballot in October – leftist former President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva and right-wing incumbent Jair Bolsonaro – have signaled they plan to extend this year’s boost in social spending into next year.”It’s a fiscal bomb,” said Sergio Goldenstein, chief strategist at Renascença DTVM. “Risk premiums look high, but there is little room for a relevant drop.”The real rate for inflation-linked government bonds has been running at the highest level since late 2016, while Brazil’s five-year credit default swaps are at highs last seen at the beginning of the pandemic in March 2020.Concerns about Brazil’s credit profile come as commodity shocks from the war in Ukraine rattle the global economy and contribute to inflation, prompting rich nations to start raising interest rates.”All the credit spreads in the world are opening, our bonds are not immune to that,” said Ronaldo Patah, chief strategist at UBS Consenso.In fact, Brazil’s strong exports of grains, oil and iron ore give it some advantages compared to other emerging markets riding out the current surge in commodity prices, independent of the political risks in Brasilia now rattling investors.Brazil’s central bank also got an early start hiking rates compared to most peers, raising its benchmark interest rate from a record low 2% in March 2021 to 13.25% currently, with another hike penciled in for August to curb double-digit inflation.Most of the market has therefore been betting on rate cuts supporting growth from the middle of next year. However, risk premiums now point to rates above 13% in the yield curve for maturities ranging from 2024 to 2033, while mid-2023 vertices indicate an accumulated rate above 14%.”I am struck by this process of (yield curve) flattening that we are seeing at a very high level”, said the chief economist at Ativa Investimentos Etore Sanchez.Roberto Dumas, chief strategist at Banco Voiter, said Brazil is caught between a central bank tightening rates while the government is finding new ways to boost spending.”The more one accelerates, the more the other needs to step on the brakes. Everyone is projecting more and more that the Selic will rise more than expected”, said Dumas, who foresees the benchmark rate at 14.25% at the end of this year.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Marcela Ayres and Jose de Castro
Editing by Brad HaynesOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .
Column: European smelter squeeze keeps zinc close to record highs
LONDON, March 29 (Reuters) – London Metal Exchange (LME) zinc recorded a new all-time high of $4,896 per tonne earlier this month, eclipsing the previous 2006 peak of $4,580 per tonne.True, the March 8 spike was over in a matter of hours and looked very much like the forced close-out of positions to cover margin calls in the LME nickel contract, which was imploding at the time before being suspended.But zinc has since re-established itself above the $4,000 level, last trading at $4,100 per tonne, amid escalating supply chain tensions.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comRussia’s invasion of Ukraine, which Moscow calls a special military operation, doesn’t have any direct impact on zinc supply as Russian exports are negligible.But the resulting increase in energy prices is piling more pressure on already struggling European smelters.European buyers are paying record physical premiums over and above record high LME prices, a tangible sign of scarcity which is now starting to spread to the North American market.The world is not yet running out of the galvanising metal but a market that even a few months ago was expected to be in comfortable supply surplus is turning out to be anything but.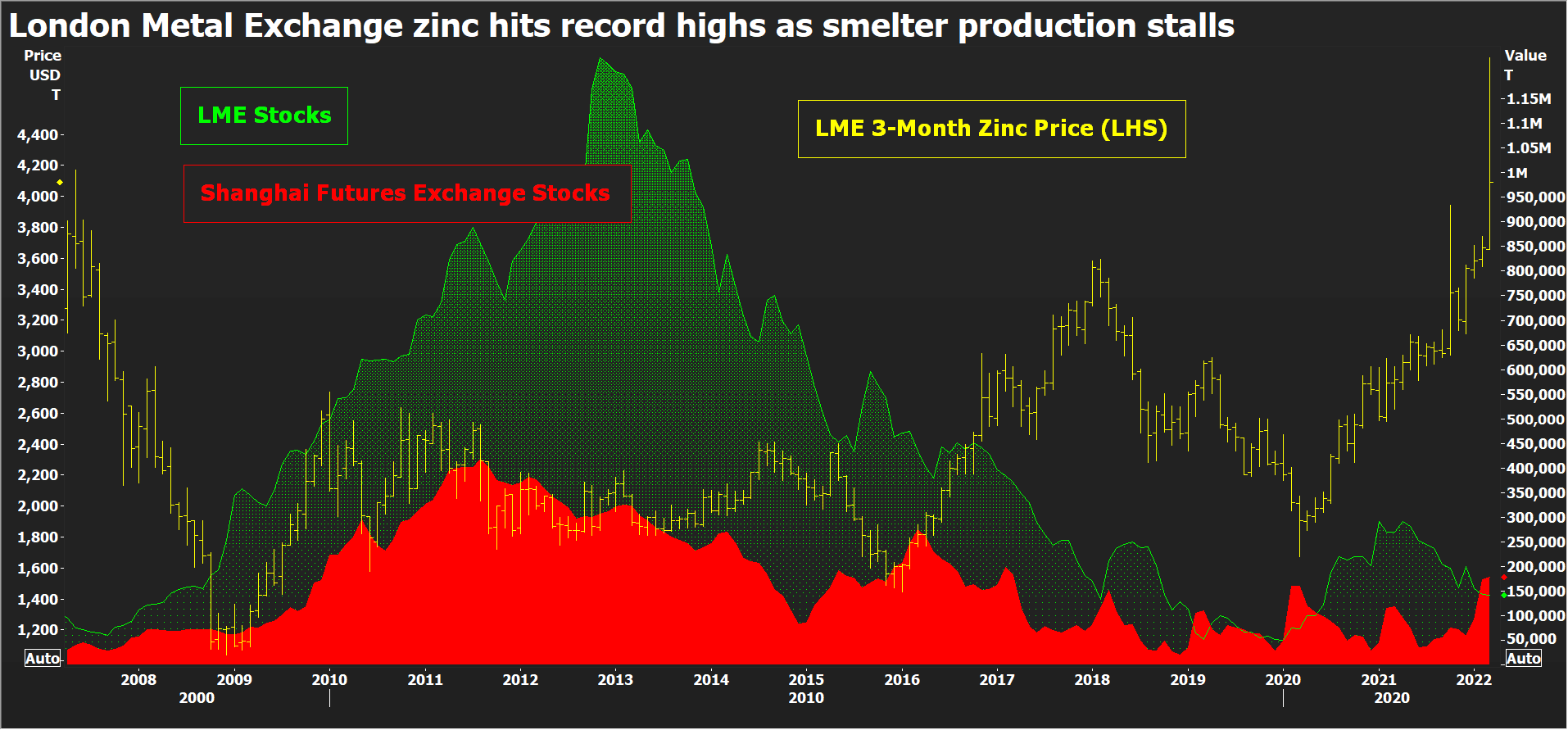 LME zinc price and stocks, Shanghai stocksEUROPEAN POWER-DOWNOne European smelter – Nyrstar’s Auby plant in France – has returned to partial production after being shuttered in January due to soaring power costs. But run-rates across the company’s three European smelters with combined annual capacity of 720,000 tonnes will continue to be flexed “with anticipated total production cuts of up to 50%”, Nyrstar said.High electricity prices across Europe mean “it is not economically feasible to operate any of our sites at full capacity”, it said.Still on full care and maintenance is Glencore’s (GLEN.L) 100,000-tonne-per-year Portovesme site in Italy, another power-crisis casualty.Zinc smelting is an energy-intensive business and these smelters were already in trouble before Russia’s invasion sent European electricity prices spiralling yet higher.Record-high physical premiums, paid on top of the LME cash price, attest to the regional shortage of metal. The premium for special-high-grade zinc at the Belgian port of Antwerp has risen to $450 per tonne from $170 last October before the winter heating crisis kicked in.The Italian premium has exploded from $215.00 to $462.50 per tonne over the same time frame, according to Fastmarkets.LME warehouses in Europe hold just 500 tonnes of zinc – all of it at the Spanish port of Bilbao and just about all of it bar 25 tonnes cancelled in preparation for physical load-out.Tightness in Europe is rippling over the Atlantic. Fastmarkets has just hiked its assessment of the U.S. Midwest physical premium by 24% to 26-30 cents per lb ($573-$661 per tonne).LME-registered stocks in the United States total a low 25,925 tonnes and available tonnage is lower still at 19,825 tonnes. This time last year New Orleans alone held almost 100,000 tonnes of zinc.
LME zinc price and stocks, Shanghai stocksEUROPEAN POWER-DOWNOne European smelter – Nyrstar’s Auby plant in France – has returned to partial production after being shuttered in January due to soaring power costs. But run-rates across the company’s three European smelters with combined annual capacity of 720,000 tonnes will continue to be flexed “with anticipated total production cuts of up to 50%”, Nyrstar said.High electricity prices across Europe mean “it is not economically feasible to operate any of our sites at full capacity”, it said.Still on full care and maintenance is Glencore’s (GLEN.L) 100,000-tonne-per-year Portovesme site in Italy, another power-crisis casualty.Zinc smelting is an energy-intensive business and these smelters were already in trouble before Russia’s invasion sent European electricity prices spiralling yet higher.Record-high physical premiums, paid on top of the LME cash price, attest to the regional shortage of metal. The premium for special-high-grade zinc at the Belgian port of Antwerp has risen to $450 per tonne from $170 last October before the winter heating crisis kicked in.The Italian premium has exploded from $215.00 to $462.50 per tonne over the same time frame, according to Fastmarkets.LME warehouses in Europe hold just 500 tonnes of zinc – all of it at the Spanish port of Bilbao and just about all of it bar 25 tonnes cancelled in preparation for physical load-out.Tightness in Europe is rippling over the Atlantic. Fastmarkets has just hiked its assessment of the U.S. Midwest physical premium by 24% to 26-30 cents per lb ($573-$661 per tonne).LME-registered stocks in the United States total a low 25,925 tonnes and available tonnage is lower still at 19,825 tonnes. This time last year New Orleans alone held almost 100,000 tonnes of zinc.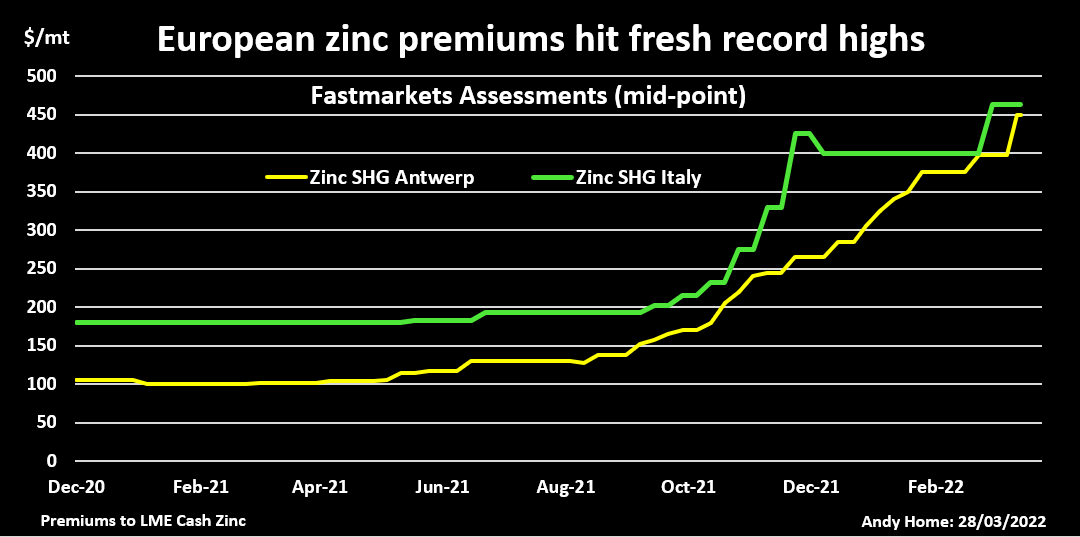 Fastmarkets Assessments of Antwerp and Italian physical zinc premiumsREBALANCING ACTAbout 80% of the LME’s registered zinc inventory is currently located at Asian locations, first and foremost Singapore, which holds 81,950 tonnes.There is also plenty of metal sitting in Shanghai Futures Exchange warehouses. Registered stocks have seen their usual seasonal Lunar New Year holiday surge, rising from 58,000 tonnes at the start of January to a current 177,826 tonnes.Quite evidently Asian buyers haven’t yet been affected by the unfolding supply crunch in Europe and there is plenty of potential for a wholesale redistribution of stocks from east to west.This is what happened last year in the lead market, China exporting its surplus to help plug gaps in the Western supply chain. Lead, however, should also serve as a warning that global rebalancing can be a slow, protracted affair due to continuing log-jams in the shipping sector.MOVING THE GLOBAL DIALWhile there is undoubted slack in the global zinc market, Europe is still big enough a refined metal producer to move the market dial.The continent accounts for around 16% of global refined output and the loss of production due to the regional energy crisis has upended the zinc market narrative.When the International Lead and Zinc Study Group (ILZSG) last met in October, it forecast a global supply surplus of 217,000 tonnes for 2021.That was already a sharp reduction from its earlier April assessment of a 353,000-tonne production overhang. The Group’s most recent calculation is that the expected surplus turned into a 194,000-tonne shortfall last year. The difference was almost wholly down to lower-than-forecast refined production growth, which came in at just 0.5% compared with an October forecast of 2.5%.With Chinese smelters recovering from their own power problems earlier in the year, the fourth-quarter deceleration was largely due to lower run-rates at Europe’s smelters.The ILZSG’s monthly statistical updates are inevitably a rear-view mirror but Europe’s production losses have continued unabated over the first quarter of 2022.Moreover, the scale of the shift higher in power pricing, not just spot but along the length of the forward curve, poses a longer-term question mark over the viability of European zinc production.A redistribution of global stocks westwards can provide some medium-term relief but zinc supply is facing a new structural challenge which is not going away any time soon.The opinions expressed here are those of the author, a columnist for Reuters.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comEditing by David ClarkeOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles.Opinions expressed are those of the author. They do not reflect the views of Reuters News, which, under the Trust Principles, is committed to integrity, independence, and freedom from bias. .
Fastmarkets Assessments of Antwerp and Italian physical zinc premiumsREBALANCING ACTAbout 80% of the LME’s registered zinc inventory is currently located at Asian locations, first and foremost Singapore, which holds 81,950 tonnes.There is also plenty of metal sitting in Shanghai Futures Exchange warehouses. Registered stocks have seen their usual seasonal Lunar New Year holiday surge, rising from 58,000 tonnes at the start of January to a current 177,826 tonnes.Quite evidently Asian buyers haven’t yet been affected by the unfolding supply crunch in Europe and there is plenty of potential for a wholesale redistribution of stocks from east to west.This is what happened last year in the lead market, China exporting its surplus to help plug gaps in the Western supply chain. Lead, however, should also serve as a warning that global rebalancing can be a slow, protracted affair due to continuing log-jams in the shipping sector.MOVING THE GLOBAL DIALWhile there is undoubted slack in the global zinc market, Europe is still big enough a refined metal producer to move the market dial.The continent accounts for around 16% of global refined output and the loss of production due to the regional energy crisis has upended the zinc market narrative.When the International Lead and Zinc Study Group (ILZSG) last met in October, it forecast a global supply surplus of 217,000 tonnes for 2021.That was already a sharp reduction from its earlier April assessment of a 353,000-tonne production overhang. The Group’s most recent calculation is that the expected surplus turned into a 194,000-tonne shortfall last year. The difference was almost wholly down to lower-than-forecast refined production growth, which came in at just 0.5% compared with an October forecast of 2.5%.With Chinese smelters recovering from their own power problems earlier in the year, the fourth-quarter deceleration was largely due to lower run-rates at Europe’s smelters.The ILZSG’s monthly statistical updates are inevitably a rear-view mirror but Europe’s production losses have continued unabated over the first quarter of 2022.Moreover, the scale of the shift higher in power pricing, not just spot but along the length of the forward curve, poses a longer-term question mark over the viability of European zinc production.A redistribution of global stocks westwards can provide some medium-term relief but zinc supply is facing a new structural challenge which is not going away any time soon.The opinions expressed here are those of the author, a columnist for Reuters.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comEditing by David ClarkeOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles.Opinions expressed are those of the author. They do not reflect the views of Reuters News, which, under the Trust Principles, is committed to integrity, independence, and freedom from bias. .
Netflix tests sharing accounts outside household
Small toy figures are seen in front of diplayed Netflix logo in this illustration taken March 19, 2020. REUTERS/Dado Ruvic/IllustrationRegister now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comMarch 16 (Reuters) – Netflix Inc is testing features including one that will allow accounts to be shared outside members’ household at an extra cost, the streaming pioneer said on Wednesday.The company is testing the features in Chile, Costa Rica and Peru allowing members on its standard and premium plans to add up to two people.Netflix is also studying another feature that will allow members on a basic, standard or premium plan to transfer their profile information to a new account or a sub account retaining data such as viewing history and personalized recommendations. (https://bit.ly/3CLKbF2)Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comThe company currently allows people who live together to share their Netflix account. However, the plans have created some confusion about when and how accounts can be shared, the company said, adding it is impacting its ability to invest in new content.The company said it would test the features for their utility before making changes in other parts of the world.Netflix in January tempered its growth expectations, projecting customer additions in the first-quarter at less than half of Wall Street’s expectations citing the late arrival of anticipated content. read more Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Akash Sriram in Bengaluru; Editing by Shailesh KuberOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .
Palm oil becomes costliest vegoil as Ukraine war halts sunoil supply
- Buyers struggle to replace sunoil quickly
- Huge demand lifts palm oil prices to a record high
- Soyoil supply limited as drought hits South America
- Palm’s premium could fade as buyers shift to soyoil
MUMBAI, March 1 (Reuters) – Palm oil has become the costliest among the four major edible oils for the first time as buyers rush to secure replacements for sunflower oil shipments from the top exporting Black Sea region that were disrupted by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.Palm oil’s record premium over rival oils could squeeze price-sensitive Asian and African consumers already reeling from spiralling fuel and food costs, and force them to curtail consumption and shift to rival soyoil , dealers said.Crude palm oil (CPO) is being offered at about $1,925 a tonne, including cost, insurance and freight (CIF), in India for March shipments, compared with $1,865 for crude soybean oil.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comRegisterCrude rapeseed oil was offered at around $1,900, while traders were not offering crude sunflower oil as ports are closed due to the Ukraine crisis.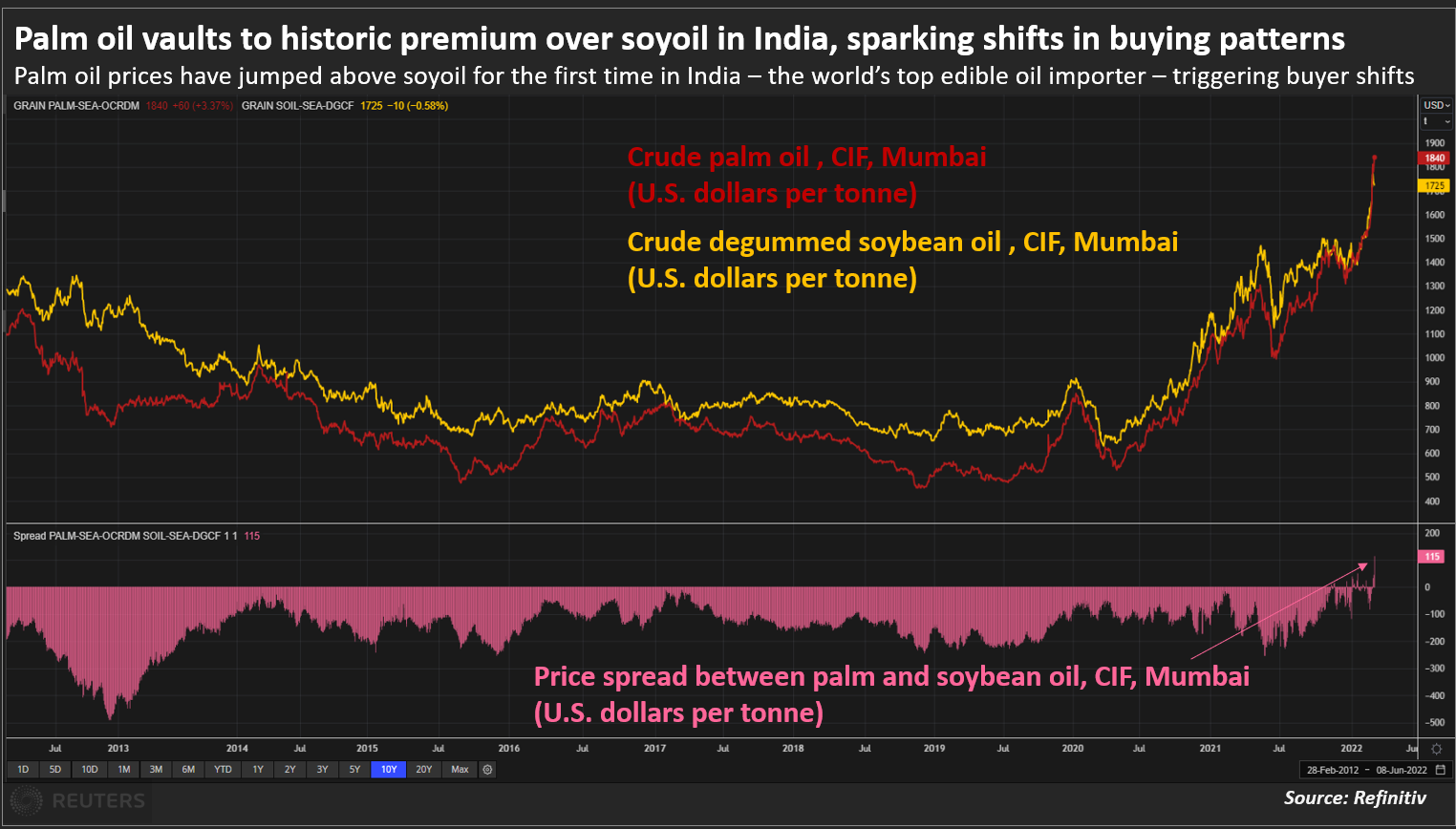 Palm oil vaults to historic premium over soyoil in India, sparking shifts in buying patternsThe Black Sea accounts for 60% of world sunflower oil output and 76% of exports. Ports in Ukraine will remain closed until the invasion ends. read more “Asian and European refiners have raised palm oil purchases for near-month shipments to replace sunoil. This buying has lifted palm oil to irrational price level,” said a Mumbai-based dealer with a global trading firm.”They have the option of buying soyoil as well. But prompt soyoil shipments are limited and they take much longer to land in Asia compared to palm oil,” he said.Soybean production in Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay is expected to fall because of dry weather. Price-sensitive Asian buyers traditionally relied on palm oil because of low costs and quick shipping times, but now they are paying more than $50 per tonne premium over soyoil and sunoil, said a Kuala Lumpur-based edible oil dealer.Palm oil’s price premium is temporary, however, and could fade in the next few weeks as buyers shift to soyoil for April shipments, the dealer said.Most of the incremental demand for palm oil is fulfilled by Malaysia, as Indonesia has put restriction on the exports, said an Indian refiner. “Malaysian stocks are depleting fast because of the surge in demand. It is the biggest beneficiary of the current geopolitical situation,” he said.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comRegisterReporting by Rajendra Jadhav
Palm oil vaults to historic premium over soyoil in India, sparking shifts in buying patternsThe Black Sea accounts for 60% of world sunflower oil output and 76% of exports. Ports in Ukraine will remain closed until the invasion ends. read more “Asian and European refiners have raised palm oil purchases for near-month shipments to replace sunoil. This buying has lifted palm oil to irrational price level,” said a Mumbai-based dealer with a global trading firm.”They have the option of buying soyoil as well. But prompt soyoil shipments are limited and they take much longer to land in Asia compared to palm oil,” he said.Soybean production in Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay is expected to fall because of dry weather. Price-sensitive Asian buyers traditionally relied on palm oil because of low costs and quick shipping times, but now they are paying more than $50 per tonne premium over soyoil and sunoil, said a Kuala Lumpur-based edible oil dealer.Palm oil’s price premium is temporary, however, and could fade in the next few weeks as buyers shift to soyoil for April shipments, the dealer said.Most of the incremental demand for palm oil is fulfilled by Malaysia, as Indonesia has put restriction on the exports, said an Indian refiner. “Malaysian stocks are depleting fast because of the surge in demand. It is the biggest beneficiary of the current geopolitical situation,” he said.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comRegisterReporting by Rajendra Jadhav
Editing by Shri NavaratnamOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .








