MUMBAI, Sept 30 (Reuters) – The Indian rupee is expected to open higher against the U.S. dollar on Friday, after the country reported a lower-than-expected current account deficit for the June quarter.The dollar index pulling back further from multi-year highs will likely be an additional boost for the rupee, traders said.The rupee is likely to open around 81.65-81.70 per dollar, up from 81.86 in the previous session.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comIndia posted a CAD of $23.9 billion in the April-June period, wider than $13.4 billion in the preceding quarter but lower than $30.5 billion that economists were expecting.In terms of percentage of the GDP, the CAD widened to 2.8%, the highest in four years. A Reuters poll of 18 economists were expecting CAD of 3.6% of the GDP.”A slightly larger services surplus, and remittances, ensured the deficit did not widen dramatically,” said Rahul Bajoria, chief India economist at Barclays Bank.Bajoria expects the CAD to remain elevated in the coming quarters, thanks to the revival in domestic demand and the ongoing impact of elevated commodity prices.Traders await the Reserve Bank of India’s policy decision at 1000 IST (0430 GMT). The surging Treasury yields and the resultant pressure on the rupee is likely to prompt the RBI reason to deliver a 50-basis-point rate hike. read more “In the context how quickly the rupee has fallen over the last few days, we think it is almost certain the RBI will deliver a 50 basis point hike and a hawkish commentary,” a trader at a Mumbai-based bank said.FTSE Russel said India will be retained on its watch list for a potential upgrade to Market Accessibility Level ‘1’ and for consideration for inclusion in the FTSE Emerging Markets Government Bond Index (EMGBI).”FTSE Russell outcome reduces the likelihood that India would be added to GBI-EM, as it suggests that there have not been sufficient progress on overcoming operational hurdles,” DBS said in a note.The dollar index dropped about 1% on Thursday to near 112, pulling back away from the two-decade high of 114.78. A rally in the British pound to above 1.10 to the dollar pulled down the gauge.KEY INDICATORS: ** One-month non-deliverable rupee forward at 81.82; onshore one-month forward premium at 26 paise** USD/INR NSE October futures closed at 82.0175 on Thursday** USD/INR forward premium for end October is 24 paise** Dollar index at 112.12** Brent crude futures down 0.3% at $88.2 per barrel** Ten-year U.S. note yield at 3.79%** SGX Nifty nearest-month futures down 0.6% at 16,715** As per NSDL data, foreign investors sold a net $255.9 million worth of Indian shares on Sept. 28** NSDL data shows foreign investors sold a net $45.8 million worth of Indian bonds on Sept. 28Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Nimesh Vora; Editing by Rashmi AichOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .
Analysis: Positive real yields may spell more trouble for U.S. stocks
A street sign for Wall Street is seen in the financial district in New York, U.S., November 8, 2021. REUTERS/Brendan McDermid/File Photo/File PhotoRegister now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comNEW YORK, April 20 (Reuters) – A hawkish turn by the Federal Reserve is eroding a key support for U.S. stocks, as real yields climb into positive territory for the first time in two years.Yields on the 10-year Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) – also known as real yields because they subtract projected inflation from the nominal yield on Treasury securities – had been in negative territory since March 2020, when the Federal Reserve slashed interest rates to near zero. That changed on Tuesday, when real yields ticked above zero. Negative real yields have meant that an investor would have lost money on an annualized basis when buying a 10-year Treasury note, adjusted for inflation. That dynamic has helped divert money from U.S. government bonds and into a broad spectrum of comparatively riskier assets, including stocks, helping the S&P 500 (.SPX) more than double from its post-pandemic low.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comAnticipation of tighter monetary policy, however, is pushing yields higher and may dent the luster of stocks in comparison to Treasuries, which are viewed as much less risky since they are backed by the U.S. government.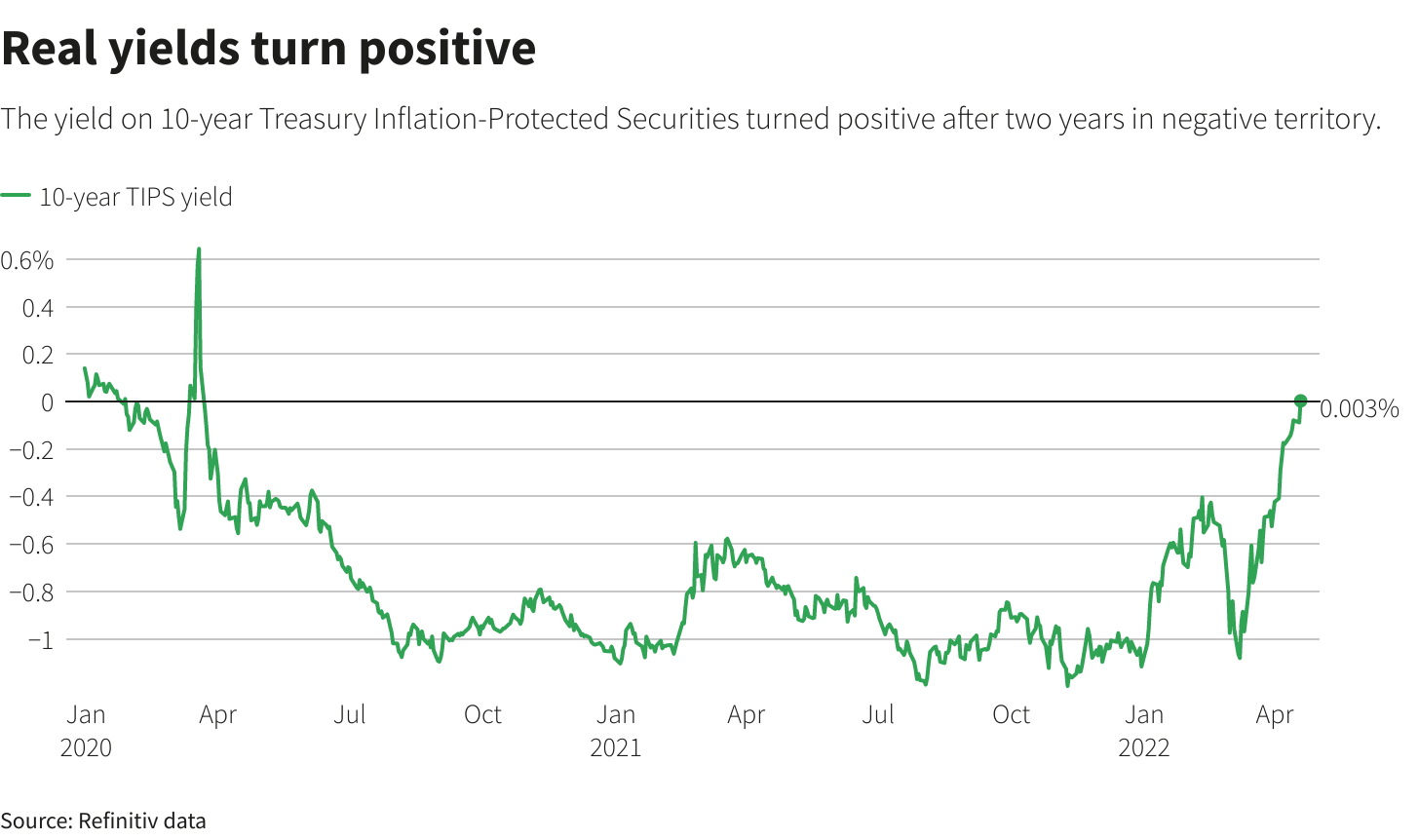 Reuters GraphicsOn Tuesday, stocks shrugged off the rise in yields, with the S&P 500 ending up 1.6% on the day. Still, the S&P 500 is down 6.4% this year, while the yield on the 10-year TIPS has climbed more than 100 basis points.”Real 10-year yields are the risk-free alternative to owning stocks,” said Barry Bannister, chief equity strategist at Stifel. “As real yield rises, at the margin it makes stocks less attractive.”One key factor influenced by yields is the equity risk premium, which measures how much investors expect to be compensated for owning stocks over government bonds.Rising yields have helped result in the measure standing at its lowest level since 2010, Truist Advisory Services said in a note last week.
Reuters GraphicsOn Tuesday, stocks shrugged off the rise in yields, with the S&P 500 ending up 1.6% on the day. Still, the S&P 500 is down 6.4% this year, while the yield on the 10-year TIPS has climbed more than 100 basis points.”Real 10-year yields are the risk-free alternative to owning stocks,” said Barry Bannister, chief equity strategist at Stifel. “As real yield rises, at the margin it makes stocks less attractive.”One key factor influenced by yields is the equity risk premium, which measures how much investors expect to be compensated for owning stocks over government bonds.Rising yields have helped result in the measure standing at its lowest level since 2010, Truist Advisory Services said in a note last week.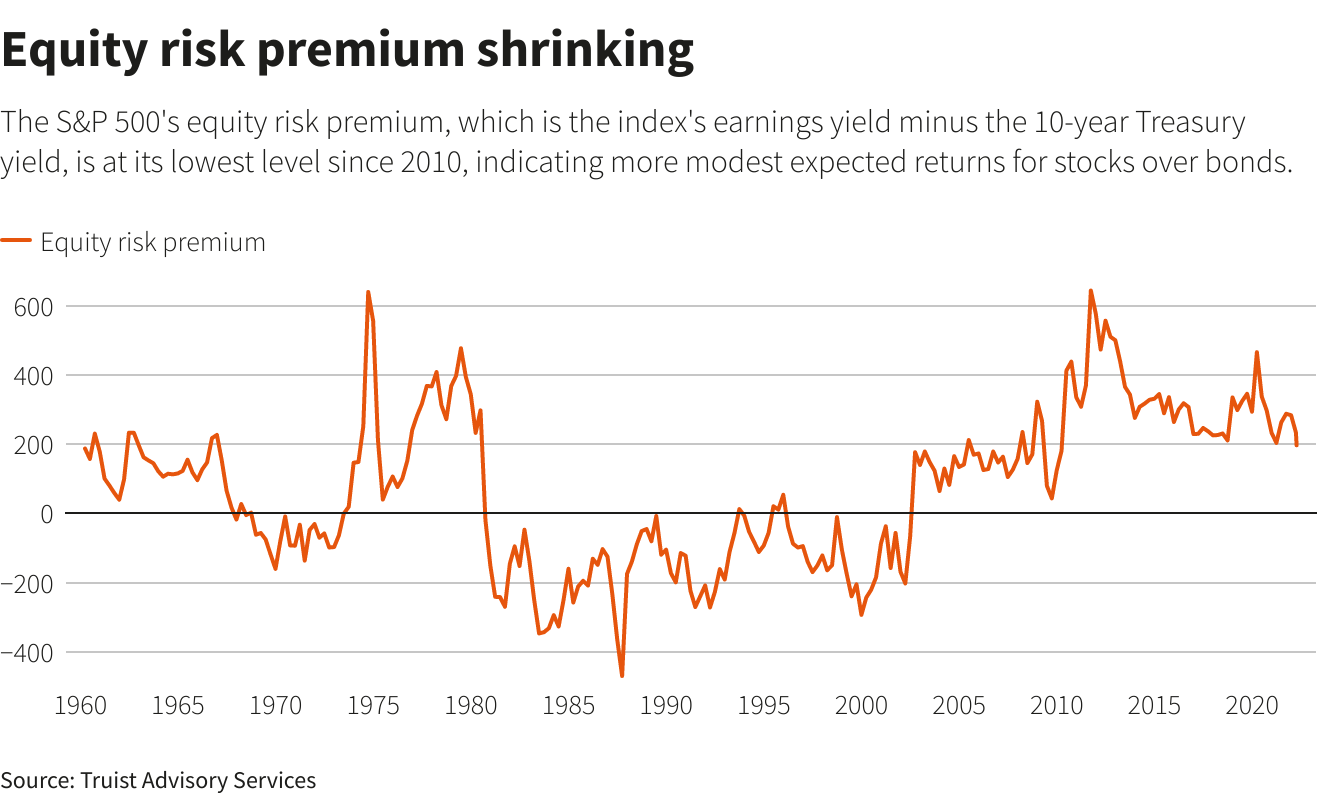 Reuters GraphicsHEADWIND TO GROWTH SHARESHigher yields in particular dull the allure of companies in technology and other high-growth sectors, with those companies’ cash flows often more weighted in the future and diminished when discounted at higher rates.That may be bad news for the broader market. The heavy presence of tech and other growth stocks in the S&P 500 means the index’s overall expected dividends are weighted in the future at close to their highest level ever, according to BofA Global Research. Five massive, high-growth stocks, for example, now make up 22% of the weight of the S&P 500.At the same time, growth shares in recent years have been highly linked to the movement of real yields.Since 2018, a ratio comparing the performance of the Russell 1000 growth index (.RLG) to its counterpart for value stocks (.RLV) – whose cash flows are more near-term – has had a negative 96% correlation with 10-year real rates, meaning they tend to move in opposite directions from growth stocks, according to Ohsung Kwon, a U.S. equity strategist at BofA Global Research.Rising yields are “a bigger headwind to equities than (they have) been in history,” he said.
Reuters GraphicsHEADWIND TO GROWTH SHARESHigher yields in particular dull the allure of companies in technology and other high-growth sectors, with those companies’ cash flows often more weighted in the future and diminished when discounted at higher rates.That may be bad news for the broader market. The heavy presence of tech and other growth stocks in the S&P 500 means the index’s overall expected dividends are weighted in the future at close to their highest level ever, according to BofA Global Research. Five massive, high-growth stocks, for example, now make up 22% of the weight of the S&P 500.At the same time, growth shares in recent years have been highly linked to the movement of real yields.Since 2018, a ratio comparing the performance of the Russell 1000 growth index (.RLG) to its counterpart for value stocks (.RLV) – whose cash flows are more near-term – has had a negative 96% correlation with 10-year real rates, meaning they tend to move in opposite directions from growth stocks, according to Ohsung Kwon, a U.S. equity strategist at BofA Global Research.Rising yields are “a bigger headwind to equities than (they have) been in history,” he said.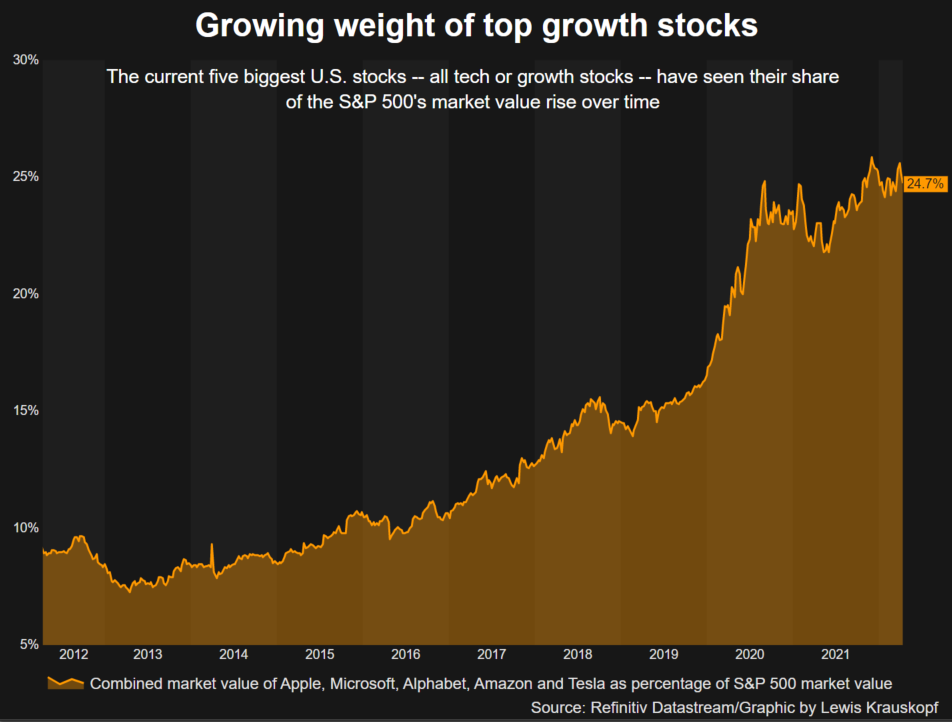 Top five stocks market cap as percentage of S&P 500Bannister estimates the S&P 500 could retest its lows of the year, which included a drop in March of 13% from the index’s record high, should the yield on the 10-year TIPS rise to 0.75% and the earnings outlook – a key component of the risk premium – remain unchanged.Lofty valuations also make stocks vulnerable if yields continue rising. Though the tumble in stocks has moderated valuations this year, the S&P 500 still trades at about 19 times forward earnings estimates, compared with a long-term average of 15.5, according to Refinitiv Datastream.“Valuations aren’t great on stocks right now. That means that capital may look at other alternatives to stocks as they become more competitive,” said Matthew Miskin, co-chief investment strategist at John Hancock Investment Management.Still, some investors believe stocks can survive just fine with rising real yields, for now. Real yields were mostly in positive territory over the past decade and ranged as high as 1.17% while the S&P 500 has climbed over 200%.JPMorgan strategists earlier this month estimated that equities could cope with 200 basis points of real yield increases. They advised clients maintain a large equity versus bond overweight.”If bond yield rises continue, they could eventually become a problem for equities,” the bank’s strategists said. “But we believe current real bond yields at around zero are not high enough to materially challenge equities.”Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Lewis Krauskopf in New York
Top five stocks market cap as percentage of S&P 500Bannister estimates the S&P 500 could retest its lows of the year, which included a drop in March of 13% from the index’s record high, should the yield on the 10-year TIPS rise to 0.75% and the earnings outlook – a key component of the risk premium – remain unchanged.Lofty valuations also make stocks vulnerable if yields continue rising. Though the tumble in stocks has moderated valuations this year, the S&P 500 still trades at about 19 times forward earnings estimates, compared with a long-term average of 15.5, according to Refinitiv Datastream.“Valuations aren’t great on stocks right now. That means that capital may look at other alternatives to stocks as they become more competitive,” said Matthew Miskin, co-chief investment strategist at John Hancock Investment Management.Still, some investors believe stocks can survive just fine with rising real yields, for now. Real yields were mostly in positive territory over the past decade and ranged as high as 1.17% while the S&P 500 has climbed over 200%.JPMorgan strategists earlier this month estimated that equities could cope with 200 basis points of real yield increases. They advised clients maintain a large equity versus bond overweight.”If bond yield rises continue, they could eventually become a problem for equities,” the bank’s strategists said. “But we believe current real bond yields at around zero are not high enough to materially challenge equities.”Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Lewis Krauskopf in New York
Editing by Ira Iosebashvili and Matthew LewisOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .
Column: Elusive bond risk premium misses its curtain call: Mike Dolan
LONDON, March 30 (Reuters) – If not now, when? Investors typically demand some added compensation for holding a security over many years to cover all the unknowables over long horizons – making the absence of such a premium in bond markets right now seem slightly bizarre.Disappearance of the so-called “term premium” in 10-year U.S. Treasury bonds over the past 5 years has puzzled analysts and policymakers and been blamed variously on subdued inflation expectations or distortions related to central bank bond buying.And yet it’s rarely, if ever, been more difficult to fathom the decade ahead – at least in terms of inflation, interest rates or indeed quantitative easing or tightening.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comInflation is running at a 40-year high after the pandemic forced wild swings in economic activity and supply bottlenecks and was then compounded by an energy price spike due to war in Ukraine that may redraw the geopolitical map.The U.S. Federal Reserve and other central banks are scrambling to normalise super easy monetary policies to cope – not really knowing whether to focus on reining in runaway prices or tackle what Bank of England chief Andrew Bailey this week described as a “historic shock” to real household incomes.Bond yields have surged, much like they did in the first quarter of last year. But this time bond funds have suffered one of their worst quarters in more than 20 years and some measures of Treasury price volatility are at their highest since banking crash of 2008. (.MOVE3M)But the most-followed estimates of term premia embedded in bond markets remain deeply negative. And this matters a lot to a whole host of critical bond market signals, not least the unfolding inversion of the U.S. Treasury curve between short and long-term yields that has presaged recessions in the past.”The 10-year term premium has barely budged even as inflation spiked to 8%, suggesting that long-dated yields are probably still capped by the Fed’s record-high balance sheet,” said Franklin Templeton’s fixed income chief Sonal Desai. “Or maybe investors think the Fed will blink and ease policy again once asset prices start a meaningful correction.””In either case, I think markets are still underestimating the magnitude of the monetary policy tightening ahead,” said Desai, adding that expectations of another more than 2 percentage points of Fed hikes this year still likely leaves real policy rates deeply negative by December even if inflation eases to 5%.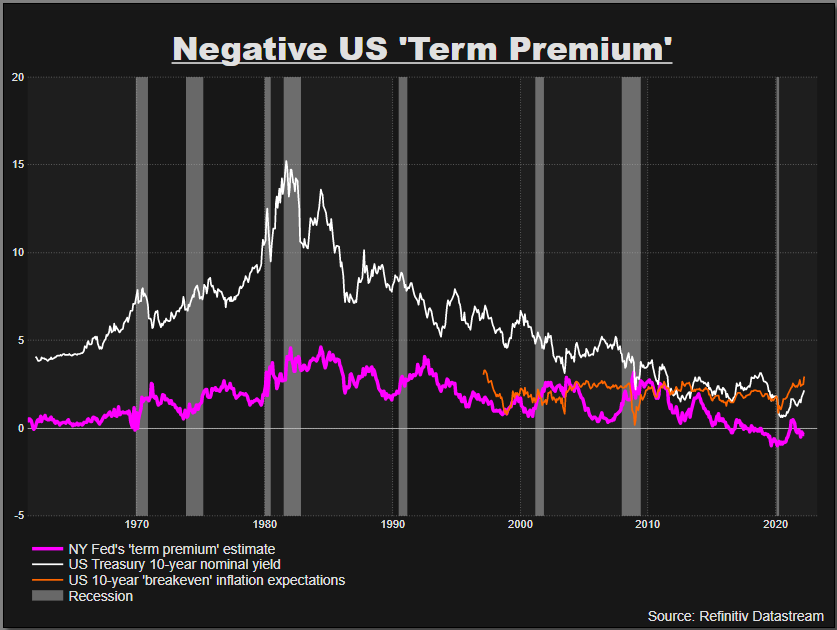 US ‘term premium’ stays negative
US ‘term premium’ stays negative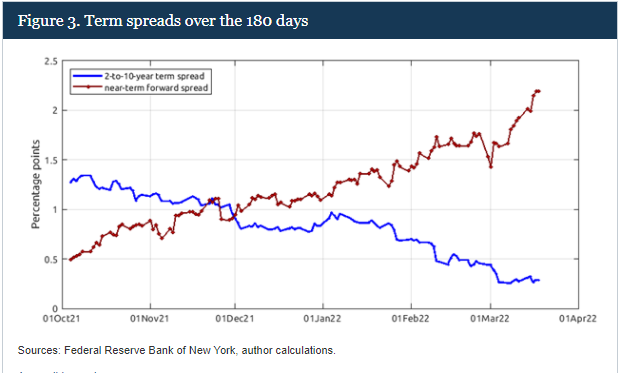 Fed contrast between Yield Curve and Near Term Forward SpreadBUMP IN THE NIGHTSo what’s the beef with the term premium?In effect, the Treasury term premium is meant to measure the additional yield demanded by investors for buying and holding a 10-year bond to maturity as opposed to buying a one year bond and rolling it over for 10 years with a new coupon.In theory it covers all the things that might go bump in the night over a decade hence – including the outside chance of credit or even political risk – but it mostly reflects uncertainty about future Fed rates and inflation expectations.At zero, you’d assume investors are indifferent to holding the 10-year today as opposed to rolling 10 one-year notes.But the New York Fed’s measure of the 10-year term premium remains deeply negative to the tune of -32 basis points – ostensibly suggesting investors actually prefer holding the longer-duration asset.Although the premium popped back positive in the first half of last year, it’s been stuck around zero or below since 2017 – oddly in the face of the Fed’s last attempt to unwind its balance sheet.And the persistent and puzzling erosion of the term premium to zero and below brings it back to the 1960s, not the much-vaunted inflation-ravaged 1970s that everyone seems to think we’re back in.It matters a lot now as the debate about the inversion of the 2-10 yield curve heats up and many argue that the signal sent by that inversion is less clear about a coming recession as it’s distorted by the disappearance of the term premium.In the absence of a term premium, the long-term yield curve is just a reflection of long-run policy rate expectations that will inevitably see some retreat if the Fed is successful in taming inflation over the next two years.Fed Board economists Eric Engstrom and Steven Sharpe late last week also dismissed the market’s obsession with a 2-10 year yield inversion signalling recession.In a blog called ‘(Don’t Fear) The Yield Curve’ they said near term forward rate spreads out to 18 months were much more informative about the chance of a looming recession, just as accurate over time and – significantly – heading in the opposite direction right now.The main reason they pushed back on the 2-10s was it contained a whole host of information about the world beyond two years that’s simply less reliable as an economic signal and “buffeted by other significant factors such as risk premiums on long-term bonds.”But what could see the term premium return?Presumably the Fed’s planned balance sheet rundown, or quantitative tightening (QT), would be a prime candidate if indeed its long-term bond buying has distorted term premia.But the last Fed attempt at QT in 2017-19 didn’t do that and Morgan Stanley thinks it will be some time yet before just allowing short-term bonds on its balance sheet to roll off and mature gets replaced by outright sales of longer-term bonds.”QT is not the opposite of QE; asset sales are.”Of course, maybe the world just hasn’t changed that much – in terms of ageing demographics, excess savings and pension fund demand, falling potential growth and negative real interest rates. Once this current storm has passed, investors seem to think that will dominate once more. read more
Fed contrast between Yield Curve and Near Term Forward SpreadBUMP IN THE NIGHTSo what’s the beef with the term premium?In effect, the Treasury term premium is meant to measure the additional yield demanded by investors for buying and holding a 10-year bond to maturity as opposed to buying a one year bond and rolling it over for 10 years with a new coupon.In theory it covers all the things that might go bump in the night over a decade hence – including the outside chance of credit or even political risk – but it mostly reflects uncertainty about future Fed rates and inflation expectations.At zero, you’d assume investors are indifferent to holding the 10-year today as opposed to rolling 10 one-year notes.But the New York Fed’s measure of the 10-year term premium remains deeply negative to the tune of -32 basis points – ostensibly suggesting investors actually prefer holding the longer-duration asset.Although the premium popped back positive in the first half of last year, it’s been stuck around zero or below since 2017 – oddly in the face of the Fed’s last attempt to unwind its balance sheet.And the persistent and puzzling erosion of the term premium to zero and below brings it back to the 1960s, not the much-vaunted inflation-ravaged 1970s that everyone seems to think we’re back in.It matters a lot now as the debate about the inversion of the 2-10 yield curve heats up and many argue that the signal sent by that inversion is less clear about a coming recession as it’s distorted by the disappearance of the term premium.In the absence of a term premium, the long-term yield curve is just a reflection of long-run policy rate expectations that will inevitably see some retreat if the Fed is successful in taming inflation over the next two years.Fed Board economists Eric Engstrom and Steven Sharpe late last week also dismissed the market’s obsession with a 2-10 year yield inversion signalling recession.In a blog called ‘(Don’t Fear) The Yield Curve’ they said near term forward rate spreads out to 18 months were much more informative about the chance of a looming recession, just as accurate over time and – significantly – heading in the opposite direction right now.The main reason they pushed back on the 2-10s was it contained a whole host of information about the world beyond two years that’s simply less reliable as an economic signal and “buffeted by other significant factors such as risk premiums on long-term bonds.”But what could see the term premium return?Presumably the Fed’s planned balance sheet rundown, or quantitative tightening (QT), would be a prime candidate if indeed its long-term bond buying has distorted term premia.But the last Fed attempt at QT in 2017-19 didn’t do that and Morgan Stanley thinks it will be some time yet before just allowing short-term bonds on its balance sheet to roll off and mature gets replaced by outright sales of longer-term bonds.”QT is not the opposite of QE; asset sales are.”Of course, maybe the world just hasn’t changed that much – in terms of ageing demographics, excess savings and pension fund demand, falling potential growth and negative real interest rates. Once this current storm has passed, investors seem to think that will dominate once more. read more 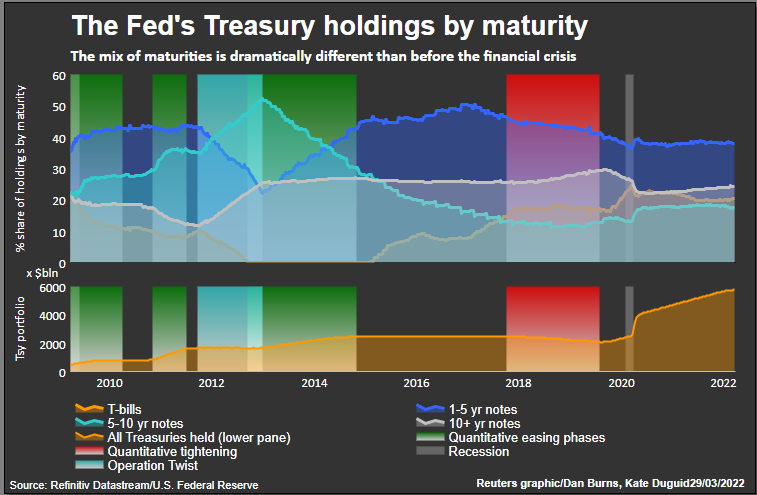 Fed balance sheet and maturitiesThe author is editor-at-large for finance and markets at Reuters News. Any views expressed here are his ownRegister now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comby Mike Dolan, Twitter: @reutersMikeD. Editing by Jane MerrimanOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles.Opinions expressed are those of the author. They do not reflect the views of Reuters News, which, under the Trust Principles, is committed to integrity, independence, and freedom from bias. .
Fed balance sheet and maturitiesThe author is editor-at-large for finance and markets at Reuters News. Any views expressed here are his ownRegister now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comby Mike Dolan, Twitter: @reutersMikeD. Editing by Jane MerrimanOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles.Opinions expressed are those of the author. They do not reflect the views of Reuters News, which, under the Trust Principles, is committed to integrity, independence, and freedom from bias. .
Nigeria offers premium to raise $1.25 billion Eurobond
Nigerian Finance Minister Zainab Ahmed attends the IMF and World Bank’s 2019 Annual Spring Meetings, in Washington, File. REUTERS/James Lawler DugganRegister now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comLAGOS/ABUJA, March 17 (Reuters) – Nigeria has priced a $1.25 billion Eurobond issue at 8.375%, its debt office said on Thursday, a premium compared to existing tenors as the country sought to raise cash to fund a costly petrol subsidy scheme in the face of limited oil revenue.The latest debt issue marks Nigeria’s eight outing on the Eurobond market after it sold a $4 billion debt in September and had been considering more issues before fears around the Omicron coronavirus variant led it to shelve plans. read more “The choice to go ahead with the Eurobond issue in the current adverse market conditions is likely connected to continued force majeure reducing oil revenue, while retained fuel subsidies are spiralling in tandem with the higher oil price,” said Mark Bohlund, senior analyst at Redd Intelligence.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comFinance Minister Zainab Ahmed told Reuters on Monday that Nigeria planned to tap 2 billion euros ($2.2 billion) this month or next of the money it raised in a eurobond sale last year and target more local borrowing in 2022 to help fund its costly petrol subsidies as oil prices rise. read more The government in January reversed a pledge to end its subsidies then, and instead extended them by 18 months amid heightened inflation to avert any protests in the run-up to presidential elections next year.At the same time, the price of oil has soared, so also has its cost as the country depends almost entirely on imports to meet its domestic gasoline needs. It also faces crude theft and vandalism in the Niger Delta, disrupting oil production.With Thursday’s bond sale, Nigeria offered more than existing eurobonds of 7.143%, creating extra debt service headache for the government struggling to boost growth with limited buffers.President Muhammadu Buhari has said the country’s deficit would rise by 1.01 trillion naira to 7.40 trillion or 4% of GDP as the government eyes new borrowing for fuel subsidy. The deficit was originally set at 3.42% of GDP.Analysts say deficit could rise above 10 trillion naira ($24 billion) in 2022 on higher fuel subsidy cost amid rising oil prices.($1 = 415.42 naira)Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comAdditional reporting by Rachel Savage in London;
Writing by Chijioke Ohuocha;
Editing by Chris Reese, Lisa Shumaker and Aurora EllisOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .








