LONDON, July 13 (Reuters) – London Metal Exchange (LME) stocks are rapidly dwindling.LME warehouses held just 696,109 tonnes of registered metal at the end of June, the lowest amount this century.Inventory halved over the first six months of the year and June’s tally was down by 1.67 million tonnes year-on-year.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comThe downtrend has further to run.Nearly 306,000 tonnes of metal were awaiting physical load-out at the end of last month. Available tonnage of all metals was just 390,280.LME shadow stocks, metal stored off-market with the option of exchange delivery, rebuilt modestly in April and May but the year-to-date increase has been a negligible 4,600 tonnes.Shrinking exchange stocks should be a bullish price signal. Right now, however, macro is trumping micro as Western recession fears pummel the industrial metals complex. The LME Index (.LMEX), which tracks the performance of the exchange’s six main base metals, has slumped by 31% from its April peak.The scale of the disconnect between price and stocks is striking. The resulting mismatch of current scarcity and expected future surplus is likely to be resolved by sporadic flare-ups in LME time-spreads.LME registered and “shadow” stocksSTOCKED OUTThis is currently happening in the LME zinc market. The cash premium over three-month metalAvailable live stocks shrunk to a depleted 14,975 tonnes at one stage in June and are still a meagre 22,475 tonnes.The rest of the headline zinc inventory of 82,200 tonnes is scheduled to depart.It also happened to sister metal lead last year, when the cash premium spiked to over $200 per tonne in August as LME on-warrant stocks fell to less than 40,000 tonnes.Time-spread tightness has been a recurring feature of the LME lead contract ever since and the cash premium is once again edging wider, ending Tuesday valued at $33 per tonne.That’s because lead stocks haven’t rebuilt in any meaningful way, currently totalling 39,250 tonnes with available tonnage at 34,850.The LME tin market has been living with depleted stocks since the start of 2021 and backwardation appears to be now hard-wired into short-dated spreads.PHYSICAL TIGHTNESSLow LME stocks of all three metals reflect extreme physical supply-chain tightness.All three have seen significant supply disruption over the last year with tin smelters hit by coronarivus lockdowns, zinc smelters in Europe powering down due to high energy prices and the Stolberg lead plant in Germany out of action since July 2021 due to flooding. read more Physical premiums for all three metals have hit record highs in Europe and the United States and remain close to those levels even as outright prices have dropped like a stone.The LME has acted as market of last resort for physical buyers and stocks will only rebuild once the supply-chain pressures pass.Chinese exports are helping rebalance both lead and zinc markets but the process is a slow one as freight and logistics bottlenecks brake arbitrage flows.
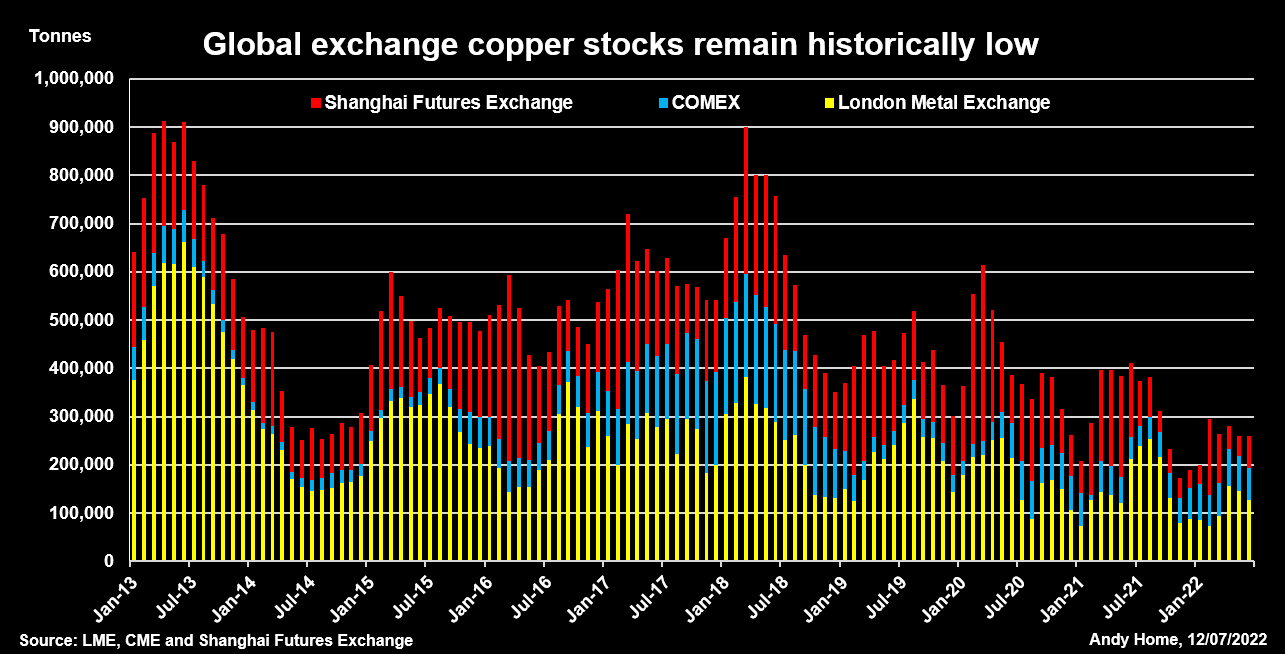 LME, CME and Shanghai Futures Exchange copper stocksCOPPER’S MUTED REBUILDCopper was stocked out last October, when live LME tonnage fell to 14,150 tonnes and the cash premium exploded to an eye-watering $1,000 per tonne.The LME intervened with lending caps and deferred delivery options, a tool-kit now extended to all its physically-deliverable contracts after the March nickel debacle.LME registered copper inventory recovered to a May peak of 180,925 tonnes but the trend has since reversed. Headline stocks have fallen back to 130,975 tonnes with fresh deliveries being offset by a string of cancellations as metal is turned around for the exit door.Indeed, combined inventory across all three major copper trading venues – LME, CME and the Shanghai Futures Exchange (ShFE)- totalled 261,000 tonnes at the end of June, up 71,000 tonnes on the start of January but down by 150,000 tonnes on June 2021.It’s a muted rebuild considering the world’s largest buyer – China – spent much of the first half of the year constrained by rolling lockdowns.
LME, CME and Shanghai Futures Exchange copper stocksCOPPER’S MUTED REBUILDCopper was stocked out last October, when live LME tonnage fell to 14,150 tonnes and the cash premium exploded to an eye-watering $1,000 per tonne.The LME intervened with lending caps and deferred delivery options, a tool-kit now extended to all its physically-deliverable contracts after the March nickel debacle.LME registered copper inventory recovered to a May peak of 180,925 tonnes but the trend has since reversed. Headline stocks have fallen back to 130,975 tonnes with fresh deliveries being offset by a string of cancellations as metal is turned around for the exit door.Indeed, combined inventory across all three major copper trading venues – LME, CME and the Shanghai Futures Exchange (ShFE)- totalled 261,000 tonnes at the end of June, up 71,000 tonnes on the start of January but down by 150,000 tonnes on June 2021.It’s a muted rebuild considering the world’s largest buyer – China – spent much of the first half of the year constrained by rolling lockdowns.LME registered and shadow aluminium stocksOFF-MARKET BUILD?Weaker Chinese demand doesn’t appear to have made any impact on ShFE copper inventory, which remains low at 69,000 tonnes, down from 129,500 tonnes a year ago.However, the headline stocks may be deceiving.The Chinese market has been rocked by another multi-pledging stocks scandal reminiscent of the Qingdao fraud of 2014.That seems to have triggered movement of both aluminium and zinc into safe-haven storage and may be deterring copper exchange deliveries.It’s quite possible that such rotation between visible and non-visible storage is accentuating the LME stocks downtrend as well.Registered aluminium stocks, for example, collapsed by 64% over the first half of the year. Live tonnage stands at just 156,300 tonnes.Yet there is no sign of tension in aluminium time-spreads, the cash-to-three-months period trading in mild contango.The market seems to be assuming that there is no shortage of aluminium despite the headline stocks figure ticking lower every day.But if metal is available, it is evidently sitting in the statistical darkness.One small clue as to its existence was a 92,000-tonne build in LME shadow aluminium stocks over the course of April and May.Such metal is primed for LME warranting if price and spreads move into the right alignment and the recent rise suggests that some metal at least is being enticed back to the paper market from the physical market.REGIONAL IMBALANCEJust about all of the shadow aluminium stocks build has occurred in Asia, which accounted for 87% of the 289,978 tonnes in this category at the end of May.LME warehouse locations in Europe held just 21,642 tonnes and U.S. ones 14,608 tonnes.The same regional skew is clear to see across all the LME base metals and is as equally true of registered stocks as it is of shadow inventory.It is a symptom of the supply and freight issues that have roiled the metals markets since the onset of COVID-19 two years ago.It is also a warning that metals supply chains are still far from functioning efficiently, even as prices bow to the weight of macro selling.The opinions expressed here are those of the author, a columnist for Reuters.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comEditing by Kirsten DonovanOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles.Opinions expressed are those of the author. They do not reflect the views of Reuters News, which, under the Trust Principles, is committed to integrity, independence, and freedom from bias. .
Insurance costs of shipping through Black Sea soar
The Arkas Line’s Conti Basel container ship is docked in the Black sea port of Odessa, Ukraine, November 4, 2016. REUTERS/Valentyn OgirenkoRegister now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comRegisterLONDON, Feb 25 (Reuters) – Insurers have raised the cost of providing cover for merchant ships through the Black Sea, adding to soaring rates to transport goods through the region for vessels still willing to sail after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.Ship owners pay annual war-risk insurance cover as well as an additional “breach” premium when entering high-risk areas. These separate premiums are calculated according to the value of the ship, or hull, for a seven-day period.Ship insurers have quoted the additional premium rate for seven days at anywhere between 1% to 2% and up to 5% of insurance costs, from an estimated 0.025% on Monday before Russia’s invasion began, according to indicative rates from marine insurance sources.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comRegisterThis would mean additional costs of hundreds of thousands of dollars for a ship voyage depending on the destination.”Given the Russian offensive from land, sea and air, it would not be surprising if some insurers will be reluctant (to provide cover),” one insurance source said.A Moldovan-flagged chemical tanker was hit by a missile on Friday near Ukraine’s port of Odessa, seriously wounding two crew.On Thursday, a Turkish-owned ship was hit by a bomb off Odessa with no casualties and the ship sailed safely into Romanian waters.Ukraine has appealed to Turkey to block Russian warships from passing through the Dardanelles and Bosphorus straits which lead to the Black Sea, after Moscow on Thursday launched a full-blown assault on Ukraine. read more Russian forces landed at Ukraine’s Black and Azov Sea ports as part of the invasion.Ukraine’s military has suspended commercial shipping at its ports although some Russian Black Sea ports remain open, including Novorossiisk, traders said on Friday.”Due to the sea invasion potential and Crimea’s location in the Black Sea, freight destined for surrounding countries will likely see re-routings and longer transit to meet its final destination,” added Glenn Koepke with supply-chain tracking platform FourKites.Mark Nugent, with shipbroker Braemar ACM, citing satellite tracking data, said a number of dry bulk vessels in the Black Sea had reversed course and were sailing towards the Bosphorus to exit the region.Freight rates have jumped after shipping companies including the world’s top container lines MSC and Maersk and many oil tanker owners suspended sailings through the region.Average earnings for smaller aframax tankers trading in the Black Sea jumped to over $100,000 a day on Thursday from $8,000 a day on Monday, shipping sources said.Earlier this month, London’s marine insurance market added the Ukrainian and Russian waters around the Black Sea and Sea of Azov to its list of areas deemed high risk, which prompted some shipping companies to hold back on sending vessels into the area. read more Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comRegisterAdditional reporting by Michael Hogan in Hamburg and Carolyn Cohn in London; Editing by Nick MacfieOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .




