Security threats are always a concern when it comes to APIs. API security can be compared to driving a car. You must be cautious and review everything closely before releasing it into the world. By failing to do so, you’re putting yourself and others at risk.
API attacks are more dangerous than other breaches. Facebook had a 50M user account affected by an API breach, and an API data breach on the Hostinger account exposed 14M customer records.
If a hacker gets into your API endpoints, it could spell disaster for your project. Depending on the industries and geographies you’re talking about, insecure APIs could get you into hot water. Especially in the EU, if you’re serving the banking, you could face massive legal and compliance problems if you’re discovered to be using insecure APIs.
To mitigate these risks, you need to be aware of the potential API vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit.
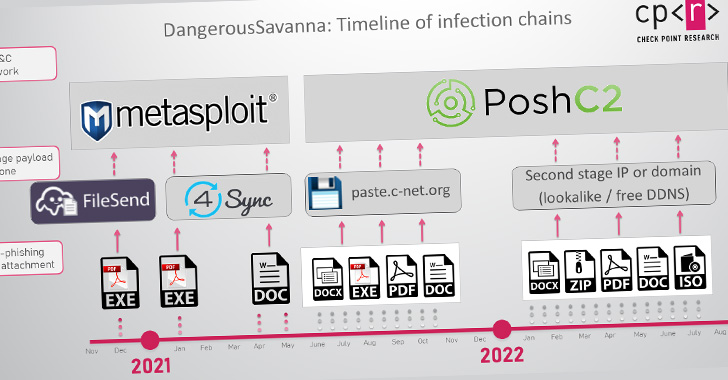
6 Commonly Overlooked API Security Risks
#1 No API Visibility and Monitoring Means’ Risk’
When you expand your use of cloud-based networks, the number of devices and APIs in use also increases. Unfortunately, this growth also leads to less visibility on what APIs you expose internally or externally.
Shadow, hidden, or deprecated APIs which fall out of your security team’s visibility create more opportunities for successful cyberattacks on unknown APIs, API parameters, and business logic. Traditional tools like API gateway lack the ability to offer a complete inventory of all APIs.
Must have API visibility, includes
- Centralized visibility as well as an inventory of all APIs
- Detailed view of API traffics
- Visibility of APIs transmitting sensitive information
- Automatic API risk analysis with predefined criteria
#2 API Incompetence
Paying attention to your API calls is important to avoid passing duplicate or repeated requests to the API. When two deployed APIs try to use the same URL, it can cause repetitive and redundant API usage problems. This is because the endpoints on both APIs are using the same URL. To avoid this, each API should have its own unique URL with optimization.
#3 Service Availability Threats
Targeted DDoS API attacks, with the help of botnets, can overload CPU cycles and processor power of the API server, sending service calls with invalid requests and making it unavailable for legitimate traffic. DDoS API attacks target not only your servers where the APIs are running but also each API endpoint.
Rate limiting grants you the confidence to maintain your applications healthy, but a good response plan comes with multi-layer security solutions like AppTrana’s API protection. The accurate and fully managed API protection continuously monitors the API traffic and instantly blocks malicious requests before reaching your server.
#4 Hesitating over API Utilization
As a B2B company, you often need to expose your internal API utilization numbers to teams outside the organization. This can be a great way to facilitate collaboration and allow others to access your data and services. However, it’s essential to carefully consider to whom you give your API access and what level of access they need. You don’t want to open your API too broadly and create security risks.
API calls need to be monitored closely when they’re shared between partners or customers. This helps ensure that everyone uses the API as intended and does not overload the system.
#5 API Injection
API injection is a term used to describe when malicious code is injected with the API request. The injected command, when executed, can even delete the user’s entire site from the server. The primary reason APIs are vulnerable to this risk is that the API developer fails to sanitize the input before it turns up in the API code.
This security loophole causes severe problems for users, including identity theft and data breaches, so it’s essential to be aware of the risk. Add input validation on the server side to prevent injection attacks and avoid executing special characters.
#6 Attacks Against IoT Devices through APIs
The effective utilization of IoT depends on the level of API security management; if that is not happening, you will have a tough time with your IoT device.
As time goes on and technology advances, hackers will always use new ways to exploit vulnerabilities in IoT products. While APIs enable powerful extensibility, they open new entrances for hackers to access sensitive data on your IoT devices. To avoid many threats and challenges IoT devices faces, APIs must be more secure.
Therefore, you need to keep your IoT devices updated with the latest security patches to ensure they are protected against the latest threats.
Stop API Risk by Implementing WAAP
In today’s world, organizations are under constant threat of API attacks. With new vulnerabilities appearing every day, it’s essential to inspect all APIs for potential threats regularly. Web application security tools are insufficient to protect your business from such risks. For API protection to work, it needs to be fully dedicated to API security. WAAP (Web Application and API Protection) can be an effective solution in this regard.
Indusface WAAP is a solution to the ever-present problem of API security. It allows you to limit the data flow to what is necessary, preventing you from accidentally leaking or exposing sensitive information. Also, the holistic Web Application & API Protection (WAAP) platform comes with the trinity of behaviour analysis, security-centric monitoring, and API management to keep malicious actions on APIs at bay.
//e&&!t&&(jQuery.ajax({url:”https://thehackernews.com/feeds/posts/default?alt=json&max-results=4″,type:”get”,cache:!1,dataType:”jsonp”,success:function(e){for(var t=””,s=””,r=0;r
.