LONDON, July 13 (Reuters) – London Metal Exchange (LME) stocks are rapidly dwindling.LME warehouses held just 696,109 tonnes of registered metal at the end of June, the lowest amount this century.Inventory halved over the first six months of the year and June’s tally was down by 1.67 million tonnes year-on-year.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comThe downtrend has further to run.Nearly 306,000 tonnes of metal were awaiting physical load-out at the end of last month. Available tonnage of all metals was just 390,280.LME shadow stocks, metal stored off-market with the option of exchange delivery, rebuilt modestly in April and May but the year-to-date increase has been a negligible 4,600 tonnes.Shrinking exchange stocks should be a bullish price signal. Right now, however, macro is trumping micro as Western recession fears pummel the industrial metals complex. The LME Index (.LMEX), which tracks the performance of the exchange’s six main base metals, has slumped by 31% from its April peak.The scale of the disconnect between price and stocks is striking. The resulting mismatch of current scarcity and expected future surplus is likely to be resolved by sporadic flare-ups in LME time-spreads.LME registered and “shadow” stocksSTOCKED OUTThis is currently happening in the LME zinc market. The cash premium over three-month metalAvailable live stocks shrunk to a depleted 14,975 tonnes at one stage in June and are still a meagre 22,475 tonnes.The rest of the headline zinc inventory of 82,200 tonnes is scheduled to depart.It also happened to sister metal lead last year, when the cash premium spiked to over $200 per tonne in August as LME on-warrant stocks fell to less than 40,000 tonnes.Time-spread tightness has been a recurring feature of the LME lead contract ever since and the cash premium is once again edging wider, ending Tuesday valued at $33 per tonne.That’s because lead stocks haven’t rebuilt in any meaningful way, currently totalling 39,250 tonnes with available tonnage at 34,850.The LME tin market has been living with depleted stocks since the start of 2021 and backwardation appears to be now hard-wired into short-dated spreads.PHYSICAL TIGHTNESSLow LME stocks of all three metals reflect extreme physical supply-chain tightness.All three have seen significant supply disruption over the last year with tin smelters hit by coronarivus lockdowns, zinc smelters in Europe powering down due to high energy prices and the Stolberg lead plant in Germany out of action since July 2021 due to flooding. read more Physical premiums for all three metals have hit record highs in Europe and the United States and remain close to those levels even as outright prices have dropped like a stone.The LME has acted as market of last resort for physical buyers and stocks will only rebuild once the supply-chain pressures pass.Chinese exports are helping rebalance both lead and zinc markets but the process is a slow one as freight and logistics bottlenecks brake arbitrage flows.
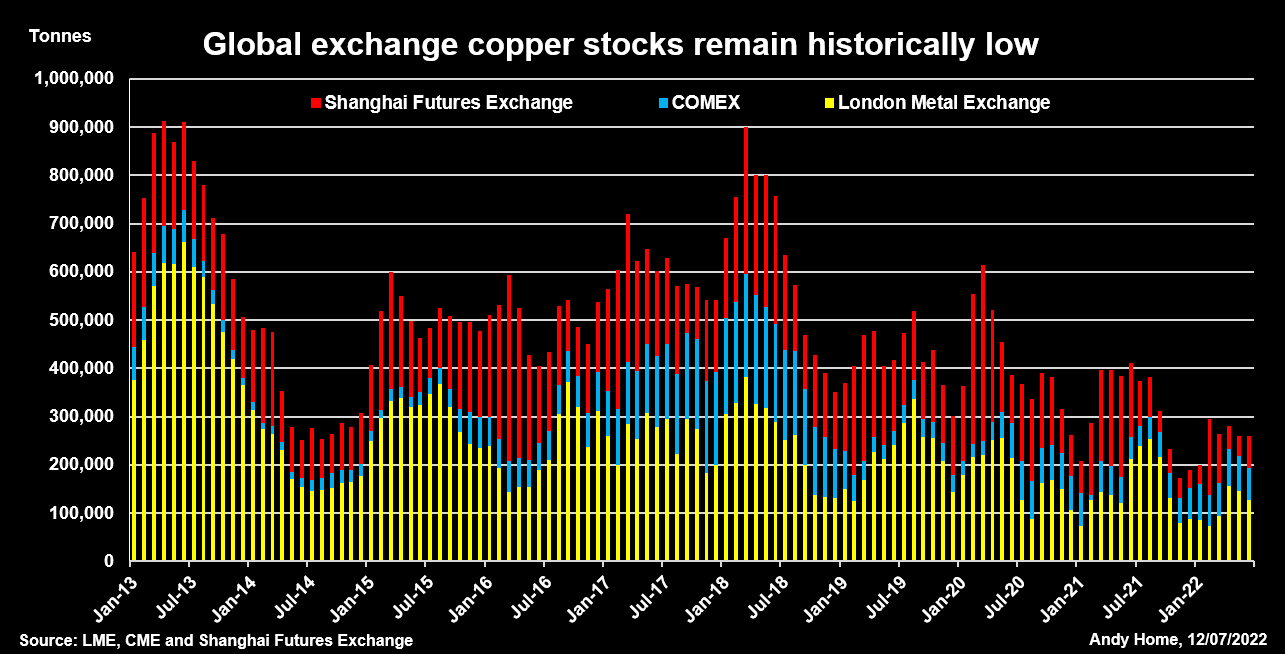 LME, CME and Shanghai Futures Exchange copper stocksCOPPER’S MUTED REBUILDCopper was stocked out last October, when live LME tonnage fell to 14,150 tonnes and the cash premium exploded to an eye-watering $1,000 per tonne.The LME intervened with lending caps and deferred delivery options, a tool-kit now extended to all its physically-deliverable contracts after the March nickel debacle.LME registered copper inventory recovered to a May peak of 180,925 tonnes but the trend has since reversed. Headline stocks have fallen back to 130,975 tonnes with fresh deliveries being offset by a string of cancellations as metal is turned around for the exit door.Indeed, combined inventory across all three major copper trading venues – LME, CME and the Shanghai Futures Exchange (ShFE)- totalled 261,000 tonnes at the end of June, up 71,000 tonnes on the start of January but down by 150,000 tonnes on June 2021.It’s a muted rebuild considering the world’s largest buyer – China – spent much of the first half of the year constrained by rolling lockdowns.
LME, CME and Shanghai Futures Exchange copper stocksCOPPER’S MUTED REBUILDCopper was stocked out last October, when live LME tonnage fell to 14,150 tonnes and the cash premium exploded to an eye-watering $1,000 per tonne.The LME intervened with lending caps and deferred delivery options, a tool-kit now extended to all its physically-deliverable contracts after the March nickel debacle.LME registered copper inventory recovered to a May peak of 180,925 tonnes but the trend has since reversed. Headline stocks have fallen back to 130,975 tonnes with fresh deliveries being offset by a string of cancellations as metal is turned around for the exit door.Indeed, combined inventory across all three major copper trading venues – LME, CME and the Shanghai Futures Exchange (ShFE)- totalled 261,000 tonnes at the end of June, up 71,000 tonnes on the start of January but down by 150,000 tonnes on June 2021.It’s a muted rebuild considering the world’s largest buyer – China – spent much of the first half of the year constrained by rolling lockdowns.LME registered and shadow aluminium stocksOFF-MARKET BUILD?Weaker Chinese demand doesn’t appear to have made any impact on ShFE copper inventory, which remains low at 69,000 tonnes, down from 129,500 tonnes a year ago.However, the headline stocks may be deceiving.The Chinese market has been rocked by another multi-pledging stocks scandal reminiscent of the Qingdao fraud of 2014.That seems to have triggered movement of both aluminium and zinc into safe-haven storage and may be deterring copper exchange deliveries.It’s quite possible that such rotation between visible and non-visible storage is accentuating the LME stocks downtrend as well.Registered aluminium stocks, for example, collapsed by 64% over the first half of the year. Live tonnage stands at just 156,300 tonnes.Yet there is no sign of tension in aluminium time-spreads, the cash-to-three-months period trading in mild contango.The market seems to be assuming that there is no shortage of aluminium despite the headline stocks figure ticking lower every day.But if metal is available, it is evidently sitting in the statistical darkness.One small clue as to its existence was a 92,000-tonne build in LME shadow aluminium stocks over the course of April and May.Such metal is primed for LME warranting if price and spreads move into the right alignment and the recent rise suggests that some metal at least is being enticed back to the paper market from the physical market.REGIONAL IMBALANCEJust about all of the shadow aluminium stocks build has occurred in Asia, which accounted for 87% of the 289,978 tonnes in this category at the end of May.LME warehouse locations in Europe held just 21,642 tonnes and U.S. ones 14,608 tonnes.The same regional skew is clear to see across all the LME base metals and is as equally true of registered stocks as it is of shadow inventory.It is a symptom of the supply and freight issues that have roiled the metals markets since the onset of COVID-19 two years ago.It is also a warning that metals supply chains are still far from functioning efficiently, even as prices bow to the weight of macro selling.The opinions expressed here are those of the author, a columnist for Reuters.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comEditing by Kirsten DonovanOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles.Opinions expressed are those of the author. They do not reflect the views of Reuters News, which, under the Trust Principles, is committed to integrity, independence, and freedom from bias. .
Column: Market turbulence won’t slow aluminium’s green drive
LONDON, May 26 (Reuters) – These are turbulent times for the global aluminium market.Aluminium has for years been characterised by chronic oversupply thanks to China’s relentless build-out of primary smelting capacity.Now, however, buyers in Europe and the United States are paying up record high premiums to get hold of physical metal.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comThe Chinese aluminium juggernaut has run out of momentum and smelters in Europe are powering down as a rolling energy crunch takes a rising toll on the region’s producers. read more London Metal Exchange (LME) stocks are disappearing to fill gaps in the supply chain. Even after its recent tumble LME three-month metal at a current $2,860 per tonne is trading at levels last seen in the great bull market of 2008.None of which, it seems, is going to slow down the drive towards green low-carbon aluminium with some of the world’s largest buyers this week committing to purchase a minimum 10% of near-zero carbon metal by 2030.GREEN ALLIANCEThe newly-formed aluminium branch of the First Movers Coalition comprises automotive companies Ford (F.N) and Volvo Group (VOLVb.ST), packaging company Ball Corp , aluminium products manufacturer Novelis (NVLXC.UL) and trade house Trafigura.The Coalition, led by the World Economic Forum and the U.S. government, is aimed at tackling carbon emissions in heavily emitting sectors such as steel, shipping and aviation. And now aluminium.The light metal is a key enabler of the green energy transition. It is a material of choice for electric vehicle (EV) battery casings and solar panels as well as offering light-weighting across multiple transport applications.However, producing aluminium is an energy-intensive process, the global sector accounting for around 2% of greenhouse gas emissions, including over one billion tonnes per year of carbon dioxide.The paradox is encapsulated in an EV battery. Aluminium accounts for only 1-2% of the cost but 17% of the carbon impact, according to Torbjörn Sternsjö, senior advisor at Swedish products group Granges, speaking at CRU’s London aluminium conference.This is a problem given ever more automakers are themselves committing to carbon-neutrality – as early as 2035 in the case of Porsche.Global aluminium production by power source 2020FROM LOW CARBON…Coal is still the globally dominant source of power for smelting aluminium, reflecting the market dominance of China, which last year accounted for around 58% of world primary output.Within China there has been a rush to swap coal-fired capacity for new plants in hydro-rich Yunnan province but spaces are fast running out and most of the country’s smelters continue to run on captive coal plants or draw energy from coal-based grids.Changing the source of power from fossil fuel to renewables is the fastest way of lowering primary aluminium’s carbon footprint.Outside of China, the rush to go green has been led by those producers with large captive hydro generation capacity.The LMEpassport for ESG accreditation now lists several aluminium producers, including Russia’s Rusal, U.S. operator Century Aluminum (CENX.O), Indonesian producer Asahan Aluminium and smelters in France (Dunkerque) and the United Kingdom (Lochaber).All have disclosed carbon equivalent footprints of 0-4 tonnes per tonne of aluminium, referencing research house CRU’s Emissions Analysis Tool.No-one yet can make it to zero on a commercial basis.The new green aluminium coalition accepts that its 10% purchase commitments for near-zero metal will be dependent on “advanced technologies not yet commercially available”….TO NO CARBONThe collective race to get to zero or near-zero aluminium is already underway, led by ELYSIS, a joint venture between Alcoa and Rio Tinto.It requires the replacement of the carbon anode in the electrolytic smelting process. The anode accounts for 1.9 tonnes of carbon per tonne of aluminium, the largest remaining carbon problem for a renewables-powered smelter, according to Tim Murray, chief executive of Cardinal Virtues Consulting, also presenting at the CRU conference.The anode being trialled in the ELYSIS process results in zero direct emissions, a much longer anode life and 15% lower costs, Alcoa chief operations officer John Slaven told delegates.If the smelter is fed with “green” alumina, the carbon impact falls below 1 tonne per tonne of metal, freight accounting for most of the residue.A processing path to near-zero primary aluminium is starting to take tangible shape.NO GREEN SANCTIONSThere has been concern that aluminium’s race to go green would be abruptly halted by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the possible sanctioning of Rusal metal.Rusal is already a major supplier of low-carbon aluminium from its hydro-powered smelters in Siberia and is itself working on inert anode technology.Fortunately for carbon-conscious buyers, the company was already put through the U.S. sanctions process in 2018, resulting in owner Oleg Deripaska (still sanctioned) giving up control of the company.That shields Rusal this time around. So too do memories of the sanctions supply-chain disruption which stretched from Guinean bauxite mines to European automakers.Rusal’s significance as a supplier, particularly to Europe, will only increase as buyers look for low-carbon metal.NO GREEN PREMIUM…YETThe First Movers Coalition is intended to create a decarbonisation tipping-point for individual sectors centred on future purchase commitments.The incentive for suppliers will be a premium for their low-carbon aluminium, according to Trafigura chief executive Jeremy Weir.Such a green premium remains conspicuous by its absence at the primary metal stage of aluminium’s process chain.And it might not appear for long at all, Colin Hamilton, commodities analyst at BMO Capital Markets, told the CRU conference.Rather, a green premium would simply be a “stepping-stone to low-carbon becoming the prime market and anything else sub-prime.”We may not have to wait much longer to find out because the drive to zero-carbon aluminium has just accelerated.The opinions expressed here are those of the author, a columnist for Reuters.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comEditing by Kirsten DonovanOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles.Opinions expressed are those of the author. They do not reflect the views of Reuters News, which, under the Trust Principles, is committed to integrity, independence, and freedom from bias. .
Japan buyers agree to Q2 aluminium premium of $172/T, sources say
Containers are seen at an industrial port in the Keihin Industrial Zone in Kawasaki, Japan September 12, 2018. REUTERS/Kim Kyung-HoonRegister now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.com
- Initial offers made by producers were $195-$250/T
- Second straight quarterly price fall
- Contrast to soaring premiums in Europe and the U.S.
TOKYO, April 7 (Reuters) – The premium for aluminium shipments to Japanese buyers for April to June was set at $172 a tonne, down 2.8% from the previous quarter, as weak demand in Japan and China outweighed concerns of supply disruptions from Russia, five sources said.The figure is lower than the $177 per tonne paid in the January-March quarter and marks a second consecutive quarterly drop. It is also lower than initial offers of $195-$250 made by producers. read more Japan is Asia’s biggest aluminium importer and the premiums for primary metal shipments it agrees to pay each quarter over the benchmark London Metal Exchange (LME) cash price set the benchmark for the region.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comThe sources, who were directly involved in pricing talks, declined to be identified because of the sensitivity of the discussions.One of them, who works at a Japanese trading house, said the decline in premiums reflected weak demand from the automobile sector as it deals with a chip shortage, as well as amply supply in Asia as China has increased exports of semi-manufactured metals.A tight container market and high freight rates also made it difficult for the metal to be shipped from Asia to Europe or North America where premiums are much higher, the source said.China is increasing exports of aluminium to fill a widening supply gap in Western markets. read more Global suppliers such as Rio Tinto (RIO.AX) and South32 (S32.AX) and Japanese manufacturers of rolled products and trading houses began price negotiations in early March. The talks took longer than usual because of uncertainty about exports from Russia as a result of sanctions following its invasion of Ukraine.Russia accounted for 17% of Japan’s total imports of primary aluminium ingots in 2021 and 6% of global aluminium supply.Concerns about the impact of disrupted Russian shipments as well as reduced output because of high power prices drove aluminium prices to a record high of $4,073.50 a tonne in early March.The duty-paid physical premiums in Europe and the United States have soared to $595 a tonne and $880 a tonne, respectively, while Asia’s spot premiums have remained around $110-170 a tonne this year, the sources said.Another of the sources said so far Russia’s Rusal had maintained shipments to Japan, which made global suppliers retreat from high initial offers.However, another of the sources said Asian supplies might get tighter as “global traders have been collecting primary aluminium from several locations in Asia and sending them to Europe or North America by chartering bulk ships to take an advantage of higher premiums”.Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.comReporting by Yuka Obayashi; Editing by Himani Sarkar and Barbara LewisOur Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. .






